how does rfid tag technology works Radio or wireless is a way of transmitting energythrough empty space—that is, instead of using a wire cable. The energyis carried by invisible waves of electricityand magnetism that vibrate through theair at the speed of light. The basic science and the practicaltechnology of wireless communication was developed in . See more Award-winning sustainable Digital Business Cards, Review Tags, Table Talkers, NFC Tags & Keychains. Our sustainable solution saves our customers money, provides a better user experience for their customers while providing great .
0 · rfid tags and their uses
1 · rfid tag working principle
2 · rfid radio frequency identification tags
3 · rfid labels how they work
4 · rfid for dummies
5 · radio frequency identification tags are
6 · how does rfid scanning work
7 · example of rfid tags
Hi everyone! I sent an email inquiry to Singtel about this. The Rep replied stating that the sim is .
Radio or wireless is a way of transmitting energythrough empty space—that is, instead of using a wire cable. The energyis carried by invisible waves of electricityand magnetism that vibrate through theair at the speed of light. The basic science and the practicaltechnology of wireless communication was developed in . See more
Imagine your mission is to design an anti-shoplifting device usingsome old radio sets you found in the garage. You could build something a bit like aradar (with a combined radio transmitter and . See moreIt's all a bit more complex than I've made it sound so far because there are, in fact, two quite different types of RF tags and they work in a slightly different way. Often the term "RFID" is loosely used to . See moreRFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the . A simple introduction to how RF and RFID tags are used in smart cards, toll collection, shop security, and other everyday applications.
RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object, animal or person.RFID tags, a technology once limited to tracking cattle, are tracking consumer products worldwide. Many manufacturers use the tags to track the location of each product they make from the time it's made until it's pulled off the shelf and tossed in a shopping cart.

rfid tags and their uses
An RFID tag is a small device that uses radio frequency signals to communicate data with a reader. RFID tags consist of several key elements: an antenna, a microchip (or integrated circuit), and a substrate that holds these components together. Unlike barcodes, which need to be scanned directly, they can be read from a distance.Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, a radio receiver, and a transmitter. RFID or radio frequency identification is a technology that facilitates the wireless discovery and tracking of any object using high-frequency radio waves. At a very basic level, RFID consists of two things: a tag and a receiver. A tag is attached to the object that needs to be identified/tracked.
Introduction. In this tutorial, we’ll explore the RFID’s origin, families, components, working principle and global frequency allocation. 2. Auto-ID Technologies. Since its establishment by MIT researchers in 1999, the realm of automatic identification technology, which we call auto-ID for short, has continuously expanded.RFID takes auto-ID technology to the next level by allowing tags to be read without line of sight and up to 30+ meters away. RFID has come a long way from its first application of identifying airplanes as friend or foe in World War II back in the 1930s.RFID readers communicate with tags through radio waves. It first emits a radio frequency signal. When the tag enters the signal range of the reader, the tag’s antenna captures the signal and activates the chip. The tag then sends the data in the chip to the reader through the antenna. An RFID tag is a tiny computer chip attached to an antenna in a compact form, transmitting information to an RFID reader through radio waves. There are several types of RFID tags, each operating at a different frequency.
A simple introduction to how RF and RFID tags are used in smart cards, toll collection, shop security, and other everyday applications.
RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object, animal or person.RFID tags, a technology once limited to tracking cattle, are tracking consumer products worldwide. Many manufacturers use the tags to track the location of each product they make from the time it's made until it's pulled off the shelf and tossed in a shopping cart.An RFID tag is a small device that uses radio frequency signals to communicate data with a reader. RFID tags consist of several key elements: an antenna, a microchip (or integrated circuit), and a substrate that holds these components together. Unlike barcodes, which need to be scanned directly, they can be read from a distance.Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, a radio receiver, and a transmitter.
RFID or radio frequency identification is a technology that facilitates the wireless discovery and tracking of any object using high-frequency radio waves. At a very basic level, RFID consists of two things: a tag and a receiver. A tag is attached to the object that needs to be identified/tracked. Introduction. In this tutorial, we’ll explore the RFID’s origin, families, components, working principle and global frequency allocation. 2. Auto-ID Technologies. Since its establishment by MIT researchers in 1999, the realm of automatic identification technology, which we call auto-ID for short, has continuously expanded.
RFID takes auto-ID technology to the next level by allowing tags to be read without line of sight and up to 30+ meters away. RFID has come a long way from its first application of identifying airplanes as friend or foe in World War II back in the 1930s.RFID readers communicate with tags through radio waves. It first emits a radio frequency signal. When the tag enters the signal range of the reader, the tag’s antenna captures the signal and activates the chip. The tag then sends the data in the chip to the reader through the antenna.
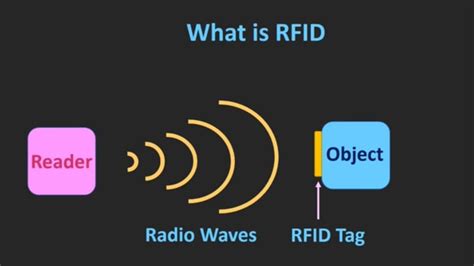
rfid tag working principle
Buy HiLetgo NFC Reader PN532 13.56mHz NFC IC Card Reader Module Kit .
how does rfid tag technology works|rfid radio frequency identification tags