rfid chip store registes RFID tags employ a chip and an antenna to broadcast information or respond when prompted to do so by an RFID reader. The chip stores the information, while the antenna responds to requests or repeatedly sends out the tag’s information for any reader within its . $39.00
0 · types of rfid systems
1 · types of rfid chips
2 · rfid definition
3 · rfid data storage
4 · rfid cards
5 · radio frequency rfid
6 · questions about rfid
7 · most common rfid files
$32.19
types of rfid systems
Learn how to store data securely on RFID cards with this comprehensive step-by-step guide. Discover RFID card types, data storage methods, and best practices for ensuring data security and operational efficiency.
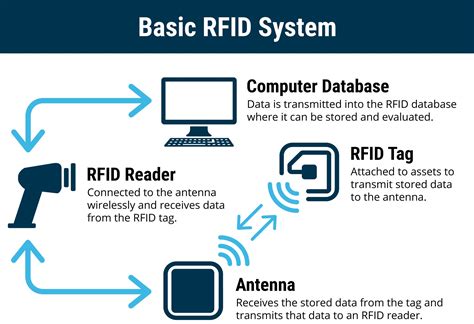
This is how they work: The reader/scanner continuously transmits a radio signal that requests the RFID chip to register. If the signal encounters the antenna of a smart tag, the chip is given a .
Learn how to store data securely on RFID cards with this comprehensive step-by-step guide. Discover RFID card types, data storage methods, and best practices for ensuring data security and operational efficiency.This is how they work: The reader/scanner continuously transmits a radio signal that requests the RFID chip to register. If the signal encounters the antenna of a smart tag, the chip is given a wake up call, so to speak. The radio waves supply it with en-ergy.
RFID tags employ a chip and an antenna to broadcast information or respond when prompted to do so by an RFID reader. The chip stores the information, while the antenna responds to requests or repeatedly sends out the tag’s information for any reader within its . RFID tags employ a chip and antenna to broadcast information or respond when prompted to do so by an RFID reader. The chip stores the information, while the antenna responds to requests or repeatedly sends out the tag’s information for any reader within its .SparkFun Qwiic RFID-IDXXLA Hookup Guide. The Qwiic RFID ID-XXLA is an I2C solution that pairs with the ID-LA modules: ID-3LA, the ID-12LA, or the ID-20LA, and utilizes 125kHz RFID chips. Let's take a look at the hardware used for this tutorial.Learn how to program RFID chips with our comprehensive guide. Discover the basics, prerequisites, and step-by-step process to efficiently program RFID chips, and explore their significance in various industries such as logistics, retail, healthcare, and manufacturing.
types of rfid chips
The NXP ICODE® family consists of high-frequency (HF) RFID chips that operate at 13.56 MHz and comply with ISO/IEC 15693 standards. These chips are well-known for their long-range readability, reliable anti-collision capabilities, and compatibility with various industry standards. RFID’s most common application within retail is tracking individual items or pieces of stock. Individual RFID tags are applied to products, and the products are then scanned, either manually by a staff member, by a fixed reader, or by a combination of both. Stores more data: RFID chips store their information in the form of Electronic Product Code (EPC) and user memory. EPC memory is used to store a specific EPC number that is associated solely with that chip and typically contains 96-128 bits, while some have more.
RFID technology helps retailers track where their inventory is and deter theft. Here’s how to use the technology in your own retail store.Learn how to store data securely on RFID cards with this comprehensive step-by-step guide. Discover RFID card types, data storage methods, and best practices for ensuring data security and operational efficiency.This is how they work: The reader/scanner continuously transmits a radio signal that requests the RFID chip to register. If the signal encounters the antenna of a smart tag, the chip is given a wake up call, so to speak. The radio waves supply it with en-ergy.
RFID tags employ a chip and an antenna to broadcast information or respond when prompted to do so by an RFID reader. The chip stores the information, while the antenna responds to requests or repeatedly sends out the tag’s information for any reader within its .
RFID tags employ a chip and antenna to broadcast information or respond when prompted to do so by an RFID reader. The chip stores the information, while the antenna responds to requests or repeatedly sends out the tag’s information for any reader within its .SparkFun Qwiic RFID-IDXXLA Hookup Guide. The Qwiic RFID ID-XXLA is an I2C solution that pairs with the ID-LA modules: ID-3LA, the ID-12LA, or the ID-20LA, and utilizes 125kHz RFID chips. Let's take a look at the hardware used for this tutorial.Learn how to program RFID chips with our comprehensive guide. Discover the basics, prerequisites, and step-by-step process to efficiently program RFID chips, and explore their significance in various industries such as logistics, retail, healthcare, and manufacturing.
The NXP ICODE® family consists of high-frequency (HF) RFID chips that operate at 13.56 MHz and comply with ISO/IEC 15693 standards. These chips are well-known for their long-range readability, reliable anti-collision capabilities, and compatibility with various industry standards. RFID’s most common application within retail is tracking individual items or pieces of stock. Individual RFID tags are applied to products, and the products are then scanned, either manually by a staff member, by a fixed reader, or by a combination of both.
Stores more data: RFID chips store their information in the form of Electronic Product Code (EPC) and user memory. EPC memory is used to store a specific EPC number that is associated solely with that chip and typically contains 96-128 bits, while some have more.
rfid definition
rfid data storage
nfc credit card entry
When communicating between an NFC reader and an NFC transponder (tag), energy .
rfid chip store registes|rfid cards