backscatter radiation rfid tags This paper presents a 5.8-GHz RFID tag that, by exploiting the quantum tunneling effect, significantly increases the range of backscatter radio links. We present an electronically simple Tunneling RFID Tag characterized by return gains as high as 35 dB with link sensitivity as low as -81 dBm. Use the nfc reader to connect a amino figure to your Nintendo 2DS.Place the .
0 · what is backscatter
1 · rfid tag backscatter
2 · rfid backscattering
3 · backscatter vs magnetic
4 · backscatter reverse link
5 · backscatter frequency
The DIY NFC Reader is a TapTo community project aiming to offer a high quality and reliable reader at a low price, which is guaranteed to work with TapTo software. Can be built yourself with the DIY NFC Reader Build .
Abstract: The interest in wearable antenna design has increased significantly due to its .
Abstract: The interest in wearable antenna design has increased significantly due to its potential applications for humans, especially in the context of RF identification (RFID) technology. RFID transponders can wirelessly transmit identification numbers or sensor data over short distances. Backscatter is a method of communication in which an RFID tag without a battery (or any internal power source) receives energy from an RFID reader’s transmission and uses that same energy to send back a reply. The tag receives the energy via electromagnetic waves propagated from the reader/antenna.ABSTRACT. This paper presents a method for measuring signal backscattering from an RFID tag and calculating tag radar cross-section (RCS), which depends on the chip input impedance. This paper presents a 5.8-GHz RFID tag that, by exploiting the quantum tunneling effect, significantly increases the range of backscatter radio links. We present an electronically simple Tunneling RFID Tag characterized by return gains as high as 35 dB with link sensitivity as low as -81 dBm.
This paper presents a method for measuring signal backscattering from RFID tags and for calculating a tag radar cross-section (RCS). We derive a theoretical formula for RCS of an RFID tag with a minimum scattering antenna and describe an experimentalBackscatter modulation of Impedance Modulated RFID tags. In a propagating wave backscatter RFID system, the reader radiates a signal which illuminates tags in its field. The tag contains no active transmitting components, but transmits its identity and data by modulating the impinging RF energy and re-radiating the modulated signal back to the .

what is backscatter
We have studied the effects of nearby objects on the read range of several types of RFID tags, and the impedance, pattern, and radiative efficiency of antennas that closely emulate the tag .Radio frequency identification (RFID) based on modulated backscatter is a wireless technology with a long history [1]. Various RFID systems use different frequency bands: low frequency (LF, 125-134 kHz), high frequency (HF, 13.56 MHz) and ultra-high frequency (UHF, 860-960 MHz).In this paper, we consider backscatter modulation-based radio-frequency identification (RFID) communication with energy harvesting tags. In this regard, we consider the effects of energy harvesting on amplified backscattering and evaluate the average read probability of the RFID tags over fading channel scenarios.
This chapter gives a detailed overview of backscatter radio frequency identification (RFID) systems. These systems are composed of an RFID reader and battery-less backscatter transponders (tags).Abstract: The interest in wearable antenna design has increased significantly due to its potential applications for humans, especially in the context of RF identification (RFID) technology. RFID transponders can wirelessly transmit identification numbers or sensor data over short distances. Backscatter is a method of communication in which an RFID tag without a battery (or any internal power source) receives energy from an RFID reader’s transmission and uses that same energy to send back a reply. The tag receives the energy via electromagnetic waves propagated from the reader/antenna.ABSTRACT. This paper presents a method for measuring signal backscattering from an RFID tag and calculating tag radar cross-section (RCS), which depends on the chip input impedance.
This paper presents a 5.8-GHz RFID tag that, by exploiting the quantum tunneling effect, significantly increases the range of backscatter radio links. We present an electronically simple Tunneling RFID Tag characterized by return gains as high as 35 dB with link sensitivity as low as -81 dBm.
This paper presents a method for measuring signal backscattering from RFID tags and for calculating a tag radar cross-section (RCS). We derive a theoretical formula for RCS of an RFID tag with a minimum scattering antenna and describe an experimentalBackscatter modulation of Impedance Modulated RFID tags. In a propagating wave backscatter RFID system, the reader radiates a signal which illuminates tags in its field. The tag contains no active transmitting components, but transmits its identity and data by modulating the impinging RF energy and re-radiating the modulated signal back to the . We have studied the effects of nearby objects on the read range of several types of RFID tags, and the impedance, pattern, and radiative efficiency of antennas that closely emulate the tag .Radio frequency identification (RFID) based on modulated backscatter is a wireless technology with a long history [1]. Various RFID systems use different frequency bands: low frequency (LF, 125-134 kHz), high frequency (HF, 13.56 MHz) and ultra-high frequency (UHF, 860-960 MHz).
In this paper, we consider backscatter modulation-based radio-frequency identification (RFID) communication with energy harvesting tags. In this regard, we consider the effects of energy harvesting on amplified backscattering and evaluate the average read probability of the RFID tags over fading channel scenarios.
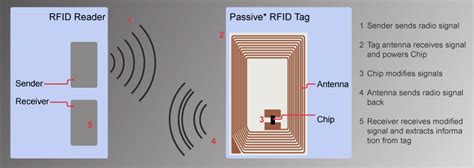
rfid tag backscatter
These NFC Tags are durable, waterproof and dustproof, suitable for challenging .
backscatter radiation rfid tags|what is backscatter