rfid read rate definition RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object, animal or person. $9.99
0 · what is rfid memory
1 · what is rfid
2 · rfid reading range
3 · rfid reading distance
4 · rfid high frequency
5 · radio frequency rfid
6 · item level rfid meaning
7 · how much does rfid cost
The National Football League playoffs for the 1999 season began on January 8, 2000. The postseason tournament concluded with the St. Louis Rams defeating the Tennessee Titans in Super Bowl XXXIV, . See more
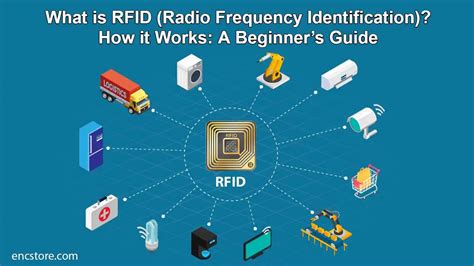
RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object, animal or person.RFID is an acronym for Radio Frequency Identification which means RFID is the wireless, non .RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object, animal or person.RFID is an acronym for Radio Frequency Identification which means RFID is the wireless, non-contact use of radio frequency waves to transfer data and identify objects, animals, or humans. RFID systems are usually comprised of an RFID reader, RFID tags, and antennas.
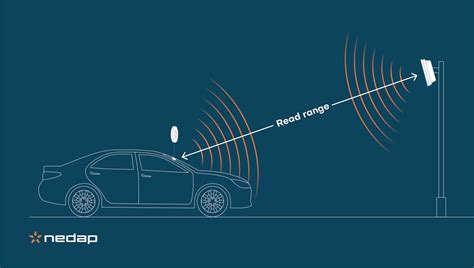
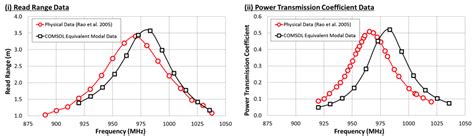
Read range refers to the distance at which an RFID reader can successfully read the information from a tag. Data storage capacity: Consider the amount of data you need to store on the tag. The data storage capacity of an RFID tag .RFID uses radio waves produced by a reader to detect the presence of (then read the data stored on) an RFID tag. Tags are embedded in small items like cards, buttons, or tiny capsules. These readers also use radio waves in some systems to write new information to the tags.Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is evolving as a major technology enabler for identifying and tracking goods and assets around the world. It can help hospitals locate expensive equipment more quickly to improve patient care, pharmaceutical companies to reduce counterfeiting and logistics providers to improve the management of moveable assets. The Truth About RFID Read Rates. Providers of passive UHF RFID solutions need to be clearer regarding the read rates, or read reliability, that end users can expect to achieve. Published: May 7, 2012 Author: Stephane Pique.
Low-frequency (LF) RFID operates at 125 to 134 KHz, offering data communication that is limited in data rate ( RFID systems comprise data-collecting readers and data-providing transponders, or tags, which are affixed to the physical objects to be tracked (see Fig. 1 ).The information stored in an RFID chip is defined by its read/write characteristics. For a read-only tag, the information stored must be recorded during the manufacturing process and cannot be typically modified or erased. RFID, or Radio Frequency Identification, is a technology that enables automatic identification and tracking of objects using radio waves. It consists of two main components – RFID tags and RFID readers.
When designing for optimum read range, you should primarily consider the reader's power, the tag's power consumption, the tag's quality factor (Q), the tag's tuning, the reader's antenna aperture, and the tag's antenna aperture.RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object, animal or person.RFID is an acronym for Radio Frequency Identification which means RFID is the wireless, non-contact use of radio frequency waves to transfer data and identify objects, animals, or humans. RFID systems are usually comprised of an RFID reader, RFID tags, and antennas.
Read range refers to the distance at which an RFID reader can successfully read the information from a tag. Data storage capacity: Consider the amount of data you need to store on the tag. The data storage capacity of an RFID tag .RFID uses radio waves produced by a reader to detect the presence of (then read the data stored on) an RFID tag. Tags are embedded in small items like cards, buttons, or tiny capsules. These readers also use radio waves in some systems to write new information to the tags.Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is evolving as a major technology enabler for identifying and tracking goods and assets around the world. It can help hospitals locate expensive equipment more quickly to improve patient care, pharmaceutical companies to reduce counterfeiting and logistics providers to improve the management of moveable assets. The Truth About RFID Read Rates. Providers of passive UHF RFID solutions need to be clearer regarding the read rates, or read reliability, that end users can expect to achieve. Published: May 7, 2012 Author: Stephane Pique.
what is rfid memory
Low-frequency (LF) RFID operates at 125 to 134 KHz, offering data communication that is limited in data rate ( RFID systems comprise data-collecting readers and data-providing transponders, or tags, which are affixed to the physical objects to be tracked (see Fig. 1 ).The information stored in an RFID chip is defined by its read/write characteristics. For a read-only tag, the information stored must be recorded during the manufacturing process and cannot be typically modified or erased. RFID, or Radio Frequency Identification, is a technology that enables automatic identification and tracking of objects using radio waves. It consists of two main components – RFID tags and RFID readers.

smart club loyalty card
what is rfid
5. Minnesota Vikings (7-2) Minnesota is the No. 5 seed in the NFC, trailing Detroit by a game for the division lead. The Vikings are the top wild-card team in the conference.
rfid read rate definition|what is rfid