frequencies for rfid tags Learn how to choose the right RFID frequency for your system with this step-by-step guide. Explore the differences between LF, HF, and UHF, and optimize performance and cost for your RFID applications. An NFC mobile payment is a contactless transaction that someone can make with their mobile device, like a smartphone or tablet. . For NFC payments to work, someone has to hold their mobile device or tap-to-pay card .
0 · what frequency does rfid use
1 · ultra high frequency rfid tags
2 · rfid radio frequency identification tags
3 · rfid radio frequency identification
4 · rfid frequency chart
5 · radio frequency identification tags are
6 · high frequency rfid tags
7 · disposable high frequency rfid tags
AFAIK the phones use a hardware called NFC controller in order to simulatate contactless .
Learn how to choose the right RFID frequency for your system with this step-by-step guide. Explore the differences between LF, HF, and UHF, and optimize performance and cost for your RFID applications.Selecting the Right Frequency for RFID Tags: The appropriate RFID tag frequency is crucial for optimizing system performance and compatibility with reader equipment. Low-frequency (LF), .Learn how to choose the right RFID frequency for your system with this step-by-step guide. Explore the differences between LF, HF, and UHF, and optimize performance and cost for your RFID applications.Selecting the Right Frequency for RFID Tags: The appropriate RFID tag frequency is crucial for optimizing system performance and compatibility with reader equipment. Low-frequency (LF), High-frequency (HF), and Ultra-high Frequency (UHF) tags offer different read ranges, data transfer rates, and anti-collision capabilities suitable for various .
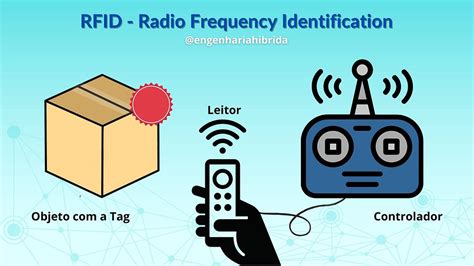
RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object, animal or person.

RFID tags are categorized according to the frequency at which they are designed to operate. Four primary frequency ranges are allocated by various government authorities for use by RFID systems. • Low frequency (LF) • High frequency (HF) • Ultra high frequency (UHF) • Microwave frequency (microwave)Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, a radio receiver, and a transmitter.
Common RFID frequencies and their respective read ranges are as follows: RFID Tags with a 10-15 Meter Read Range. Many people often ask if there are RFID tags that can be read from a distance of 10 meters or more. For applications that require medium to long-range reading, UHF tags are generally the best choice.This blog will delve into the common RFID frequency ranges as well as its advantages, disadvantages, and application scenarios. RFID-enhanced labels have specific properties based on the type of tags and the frequency on which they operate. We will review the frequencies and some of the behavioral properties of those tags in this post.The most common RFID frequencies used for RFID applications are: Low frequency (9-135 KHz) High frequency (13.553-15.567 MHz) Amateur radio band (430-440 MHz) Ultra-high frequency (860-930 MHz) Microwave (2.4-2.4835 GHz, 5.8 GHz)
what frequency does rfid use
This article will analyze in detail the characteristics and application differences of the three RFID frequencies: LF (low frequency), HF (high frequency), and UHF (ultra-high frequency).Learn how to choose the right RFID frequency for your system with this step-by-step guide. Explore the differences between LF, HF, and UHF, and optimize performance and cost for your RFID applications.Selecting the Right Frequency for RFID Tags: The appropriate RFID tag frequency is crucial for optimizing system performance and compatibility with reader equipment. Low-frequency (LF), High-frequency (HF), and Ultra-high Frequency (UHF) tags offer different read ranges, data transfer rates, and anti-collision capabilities suitable for various .
RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object, animal or person.RFID tags are categorized according to the frequency at which they are designed to operate. Four primary frequency ranges are allocated by various government authorities for use by RFID systems. • Low frequency (LF) • High frequency (HF) • Ultra high frequency (UHF) • Microwave frequency (microwave)Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, a radio receiver, and a transmitter.Common RFID frequencies and their respective read ranges are as follows: RFID Tags with a 10-15 Meter Read Range. Many people often ask if there are RFID tags that can be read from a distance of 10 meters or more. For applications that require medium to long-range reading, UHF tags are generally the best choice.
This blog will delve into the common RFID frequency ranges as well as its advantages, disadvantages, and application scenarios.
RFID-enhanced labels have specific properties based on the type of tags and the frequency on which they operate. We will review the frequencies and some of the behavioral properties of those tags in this post.
The most common RFID frequencies used for RFID applications are: Low frequency (9-135 KHz) High frequency (13.553-15.567 MHz) Amateur radio band (430-440 MHz) Ultra-high frequency (860-930 MHz) Microwave (2.4-2.4835 GHz, 5.8 GHz)
rfid tag
rain rfid standard
ultra high frequency rfid tags
rfid radio frequency identification tags
Google Pay™ is a fast, simple way to make contactless payments. You can tap to .
frequencies for rfid tags|rfid radio frequency identification tags