rfid tag user memory RFID tags store a lot of data in their memory - that's what makes them so useful. While there . 2022–23 NFL playoffs. The National Football League playoffs for the 2022 season began on January 14, 2023, and concluded with Super Bowl LVII on February 12 at State Farm Stadium .
0 · rfid tag memory
1 · rfid tag identification
2 · rfid tag data types
3 · rfid tag data storage
4 · rfid gen2 memory bank
5 · rfid gen2 layout
6 · rfid epc dsfid
7 · rfid epc 16
Near-field communication (NFC) is a set of communication protocols that enables communication between two electronic devices over a distance of 4 cm (1+1⁄2 in) or less. NFC offers a low-speed connection through a simple setup that can be used for the bootstrapping of capable wireless connections. Like other proximity card technologies, NFC is based on inductive coupling between two electromagnetic coilsMethod 2: Looking for signs on the card: Some cards may have visible indications indicating the presence of RFID or NFC technology. Look for any logos or symbols on the card that suggest contactless communication. .
rfid tag memory
Understand memory layout for Gen2 UHF (RAIN) RFID tags including the memory banks for EPC, User Memory, Access and TID along with key commands for security.
rfid tag identification
User memory in RFID tags can range from a few bytes to several kilobytes, . The user memory in an RFID tag is provided to add extra information about the .
RFID tags store a lot of data in their memory - that's what makes them so useful. While there .User memory is an additional memory bank available on some RFID tags, separate from the . When someone programs an RFID tag, most of the time they are writing data to .
An ultrahigh-frequency Gen 2 RFID tag carries business data in two memory .
User memory. When starting your application and selecting an RFID tag, in order .The data on UHF RFID labels is stored in different ‘memory banks’, two of which are the .
rfid tag data types
rfid tag data storage
add business cards to smart phone contacts
When starting your application and selecting an RFID tag, in order to know about how much .
Understand memory layout for Gen2 UHF (RAIN) RFID tags including the memory banks for EPC, User Memory, Access and TID along with key commands for security.
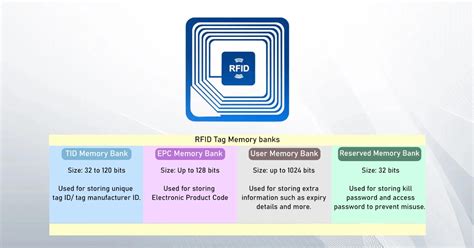
User memory in RFID tags can range from a few bytes to several kilobytes, depending on the tag type. Larger user memory enables more complex data to be stored, enabling sophisticated use cases. The user memory in an RFID tag is provided to add extra information about the product such as expiry or color/size. The size of user memory could be anything between 0 to 128 bytes (0-1024 bits) and the higher the tag, the higher the storage capacity.
RFID tags store a lot of data in their memory - that's what makes them so useful. While there can be many different types of identifying information stored in tags (which can vary from industry to industry), the majority of that is beyond the scope of this tutorial.User memory is an additional memory bank available on some RFID tags, separate from the EPC memory. It allows businesses to store custom data beyond the EPC, such as product descriptions, manufacturing dates, batch numbers, or other relevant information.
When someone programs an RFID tag, most of the time they are writing data to the EPC memory, or in a few cases, the user memory. 2 Main Reasons You Should Encode Your RFID Tags. Encoding your RFID tags becomes very important in a couple of different scenarios common in the RFID industry: An ultrahigh-frequency Gen 2 RFID tag carries business data in two memory banks: the EPC memory bank (also called the UII memory bank) and the user memory bank. User memory. When starting your application and selecting an RFID tag, in order to know about how much memory is on each tag's IC, you can check the specifications page on each tag's data sheet. Or take a look at our UHF IC RFID Comparison Guide.
The data on UHF RFID labels is stored in different ‘memory banks’, two of which are the Electronic Product Code (EPC) memory and User memory. Let’s explore what these memory banks are and how they differ from each other. Understanding EPC Memory. EPC memory, or Electronic Product Code memory, is one of the fundamental components of UHF RFID labels.When starting your application and selecting an RFID tag, in order to know about how much memory is on each tag’s IC, you can check the specifications page on each tag’s data sheet. To learn the properties of each memory bank, we have outlined them below: Reserved Memory:Understand memory layout for Gen2 UHF (RAIN) RFID tags including the memory banks for EPC, User Memory, Access and TID along with key commands for security.
User memory in RFID tags can range from a few bytes to several kilobytes, depending on the tag type. Larger user memory enables more complex data to be stored, enabling sophisticated use cases. The user memory in an RFID tag is provided to add extra information about the product such as expiry or color/size. The size of user memory could be anything between 0 to 128 bytes (0-1024 bits) and the higher the tag, the higher the storage capacity.RFID tags store a lot of data in their memory - that's what makes them so useful. While there can be many different types of identifying information stored in tags (which can vary from industry to industry), the majority of that is beyond the scope of this tutorial.
User memory is an additional memory bank available on some RFID tags, separate from the EPC memory. It allows businesses to store custom data beyond the EPC, such as product descriptions, manufacturing dates, batch numbers, or other relevant information.
When someone programs an RFID tag, most of the time they are writing data to the EPC memory, or in a few cases, the user memory. 2 Main Reasons You Should Encode Your RFID Tags. Encoding your RFID tags becomes very important in a couple of different scenarios common in the RFID industry:
An ultrahigh-frequency Gen 2 RFID tag carries business data in two memory banks: the EPC memory bank (also called the UII memory bank) and the user memory bank. User memory. When starting your application and selecting an RFID tag, in order to know about how much memory is on each tag's IC, you can check the specifications page on each tag's data sheet. Or take a look at our UHF IC RFID Comparison Guide.
The data on UHF RFID labels is stored in different ‘memory banks’, two of which are the Electronic Product Code (EPC) memory and User memory. Let’s explore what these memory banks are and how they differ from each other. Understanding EPC Memory. EPC memory, or Electronic Product Code memory, is one of the fundamental components of UHF RFID labels.
rfid gen2 memory bank
rfid gen2 layout
2018 Season 2024 Season . NFC Wild Card Playoff, AT&T Stadium, Arlington, TX. Recap; .Fast, updating NFL football game scores and stats as games are in progress are provided by CBSSports.com.
rfid tag user memory|rfid gen2 layout