uhf rfid use cases A UHF RFID reader is a device that can communicate with RFID tags working in the ultra-high frequency band. It can not only read the information stored on the tag but also write new data to the tag, realizing wireless transmission and update of data.
A digital car key relies on NFC (Near Field Communication) or UWB (Ultra-Wide Band) to authenticate your identity and start your car. If you have an NFC-compatible Android phone, position your .
0 · ultra high frequency rfid tags
1 · ultra high frequency rfid
2 · uhf rfid definition
3 · rfid tags in humans
4 · radio frequency identification tag
5 · radio frequency identification rfid system
6 · radio frequency identification rfid reader
7 · how does uhf rfid work
Fans can listen to free, live streaming audio of Auburn Sports Network radio broadcasts of Tiger games and coach's shows. Listen on. Computer; Radio; Mobile App; .
When an RFID reader emits radio waves, the tags within range respond by transmitting their unique identification information back to the reader. The applications of UHF RFID are vast and varied, spanning across industries such as retail, logistics, healthcare, . For anyone to make that call while also being ready to capitalize on new . When an RFID reader emits radio waves, the tags within range respond by transmitting their unique identification information back to the reader. The applications of UHF RFID are vast and varied, spanning across industries such as retail, logistics, healthcare, manufacturing, and more. For anyone to make that call while also being ready to capitalize on new technology, it’s essential to understand the differences and similarities between ambient IoT and UHF RFID and to fully understand how to strategically deploy each or .
Among the forefront applications of RFID are the following leading use cases: 1. Supply chain tracking. RFID technology is extensively utilized in supply chain tracking to enable the real-time visibility and traceability of goods throughout the supply chain process.
A UHF RFID reader is a device that can communicate with RFID tags working in the ultra-high frequency band. It can not only read the information stored on the tag but also write new data to the tag, realizing wireless transmission and update of data. UHF RFID offers the ability to build in flexibility to a manufacturing line. If a retool may be in the future, or carriers cannot be precisely positioned, a UHF system can provide extra coverage to account for any small differences in positioning. UHF RFID use cases include: NFC is typically recommended for: • Retail inventory management • Logistics and supply chain asset tracking • Manufacturing production process tracking for equipment, tools, and raw materials • Tracking medical equipment in healthcare • Transportation (vehicle identification, fleet management, toll collection)
UHF RFID: Taking Manufacturing Visibility and Control to the Next Level. Guidelines for Deploying the UHF EPC Gen2 RFID Air Interface to Boost the Reach and Capabilities of Identification Applications in Manufacturing. Abstract. High-frequency (HF) RFID solutions have a complementary technology in ultra-high frequency (UHF) RFID.
Carlotal 860-960 MHz UHF, Alien Higgs® 4, Custom RFID Tag, Industrial RFID Tag, On-Metal RFID Tag. Discover the characteristics, uses, and benefits of UHF RFID tags in various industries like retail and logistics. A best practice for this use case is to mount UHF RFID scanners in fixed locations, such as a warehouse entrance and exit points. Items are then automatically registered and tracked when brought onto or removed from the premises.Inventory management, asset tracking and authentication solutions are just some of the use cases being enabled by RFID in retail, logistics, supply chain, healthcare, airline baggage, automotive and manufacturing. When an RFID reader emits radio waves, the tags within range respond by transmitting their unique identification information back to the reader. The applications of UHF RFID are vast and varied, spanning across industries such as retail, logistics, healthcare, manufacturing, and more.
For anyone to make that call while also being ready to capitalize on new technology, it’s essential to understand the differences and similarities between ambient IoT and UHF RFID and to fully understand how to strategically deploy each or . Among the forefront applications of RFID are the following leading use cases: 1. Supply chain tracking. RFID technology is extensively utilized in supply chain tracking to enable the real-time visibility and traceability of goods throughout the supply chain process.A UHF RFID reader is a device that can communicate with RFID tags working in the ultra-high frequency band. It can not only read the information stored on the tag but also write new data to the tag, realizing wireless transmission and update of data. UHF RFID offers the ability to build in flexibility to a manufacturing line. If a retool may be in the future, or carriers cannot be precisely positioned, a UHF system can provide extra coverage to account for any small differences in positioning.
UHF RFID use cases include: NFC is typically recommended for: • Retail inventory management • Logistics and supply chain asset tracking • Manufacturing production process tracking for equipment, tools, and raw materials • Tracking medical equipment in healthcare • Transportation (vehicle identification, fleet management, toll collection)
ultra high frequency rfid tags
ultra high frequency rfid


UHF RFID: Taking Manufacturing Visibility and Control to the Next Level. Guidelines for Deploying the UHF EPC Gen2 RFID Air Interface to Boost the Reach and Capabilities of Identification Applications in Manufacturing. Abstract. High-frequency (HF) RFID solutions have a complementary technology in ultra-high frequency (UHF) RFID.
Carlotal 860-960 MHz UHF, Alien Higgs® 4, Custom RFID Tag, Industrial RFID Tag, On-Metal RFID Tag. Discover the characteristics, uses, and benefits of UHF RFID tags in various industries like retail and logistics.
A best practice for this use case is to mount UHF RFID scanners in fixed locations, such as a warehouse entrance and exit points. Items are then automatically registered and tracked when brought onto or removed from the premises.
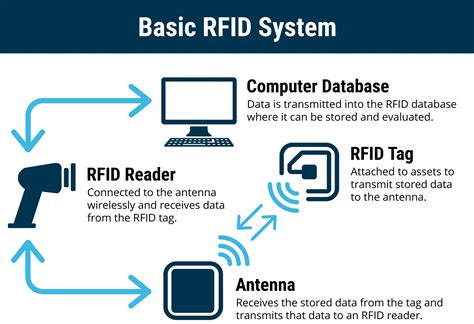
uhf rfid definition
rfid tags in humans
ACS ACR122U-SDK NFC Contactless Smart Card Reader Software Development Kit. $ 149.00. Out of stock. 13.56MHz RFID NFC reader writer ISO14443 ISO18092. Supports MOST Card, Mifare, NTAG, Ultralight, .
uhf rfid use cases|ultra high frequency rfid