uhf rfid is beeter than rfid only Ambient IoT is relatively new compared to UHF RFID, the latest version of which was standardized at the turn of the millennium. While the technology further amplifies the benefits created by RFID through improved supply chain visibility, on the surface they appear very . What's the recommended MOO Business Card size in pixels? If you're uploading .
0 · rfid vs low frequency
1 · rfid frequency
2 · low frequency rfid range
3 · high frequency rfid tags
4 · high frequency rfid 12 inch
5 · hf rf frequency
$7.95
Ambient IoT is relatively new compared to UHF RFID, the latest version of which was standardized at the turn of the millennium. While the technology further amplifies the benefits created by RFID through improved supply chain visibility, on the surface they appear very . Ambient IoT is relatively new compared to UHF RFID, the latest version of which was standardized at the turn of the millennium. While the technology further amplifies the benefits created by RFID through improved supply chain visibility, .
rfid door lock access control system kit electric lock new
Low Frequency RFID & High Frequency RFID have 8 key differences that set them apart - the actual frequency range , data rates, write capabilities, environmental concerns, read range, tag formats, RFID applications, RFID hardware. Comparing ultra-high-frequency (UHF) vs. high-frequency (HF) vs. near field communication (NFC) vs. low-frequency (LF) RFID tag types. An explanation of the difference between active, passive and semi-passive RFID tags. RFID operates across three primary frequency bands: Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra-High Frequency (UHF). In this guide, we’ll explore the characteristics of each band, their applications, and how to choose the one that best fits your needs.
Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) tags. The majority of UHF systems operate between 860 and 960 megahertz. The distances for UHF tags are usually measured in feet and meters. While the tags are an excellent fit for objects that require fast identification from a distance, the tags are significantly impacted by liquids.
rfid hospital system code
The two RFID frequency bands, HF vs UHF, have obvious differences in terms of application areas, technical characteristics and advantages. When enterprises choose to use which RFID frequency band, should fully consider their own needs and the performance and cost trade-offs. UHF RFID technology has gained popularity due to its superior read-range capabilities, allowing for long-distance communication between RFID readers and tags. UHF RFID tags consist of a microchip that stores unique identification data and an antenna that enables communication with RFID readers.RFID HF operates in the High-Frequency range of 13.56 MHz, while RFID UHF operates in the Ultra-High Frequency range of 860-960 MHz. The variation in frequency is a fundamental distinction that leads to various differences in their applications and performances.Low-Frequency (LF) The low-frequency band is able to cover frequencies from 30 KHz (Kilohertz) to 300 KHz. Usually, low-frequency RFID systems operate right around 125 KHz. The low-frequency band has a slower read speed than higher frequencies, but it has a greater ability to be transmitted or received in all directions.
victorinox lifestyle accessories 4.0 gear sling with rfid protection
Whether you are considering using high frequency (HF) RFID technologies or ultra high frequency (UHF) Gen 2, the first question you must ask yourself is why? This article provides information to help you make informed choices on tags and technology.
Ambient IoT is relatively new compared to UHF RFID, the latest version of which was standardized at the turn of the millennium. While the technology further amplifies the benefits created by RFID through improved supply chain visibility, . Low Frequency RFID & High Frequency RFID have 8 key differences that set them apart - the actual frequency range , data rates, write capabilities, environmental concerns, read range, tag formats, RFID applications, RFID hardware. Comparing ultra-high-frequency (UHF) vs. high-frequency (HF) vs. near field communication (NFC) vs. low-frequency (LF) RFID tag types. An explanation of the difference between active, passive and semi-passive RFID tags. RFID operates across three primary frequency bands: Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra-High Frequency (UHF). In this guide, we’ll explore the characteristics of each band, their applications, and how to choose the one that best fits your needs.
Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) tags. The majority of UHF systems operate between 860 and 960 megahertz. The distances for UHF tags are usually measured in feet and meters. While the tags are an excellent fit for objects that require fast identification from a distance, the tags are significantly impacted by liquids.
The two RFID frequency bands, HF vs UHF, have obvious differences in terms of application areas, technical characteristics and advantages. When enterprises choose to use which RFID frequency band, should fully consider their own needs and the performance and cost trade-offs.
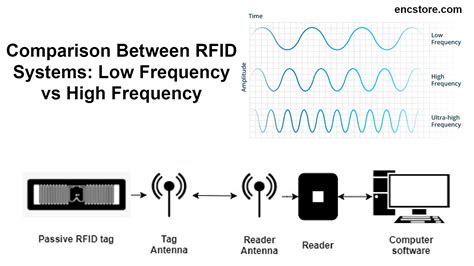
UHF RFID technology has gained popularity due to its superior read-range capabilities, allowing for long-distance communication between RFID readers and tags. UHF RFID tags consist of a microchip that stores unique identification data and an antenna that enables communication with RFID readers.RFID HF operates in the High-Frequency range of 13.56 MHz, while RFID UHF operates in the Ultra-High Frequency range of 860-960 MHz. The variation in frequency is a fundamental distinction that leads to various differences in their applications and performances.
rfid vs low frequency
rfid frequency
Low-Frequency (LF) The low-frequency band is able to cover frequencies from 30 KHz (Kilohertz) to 300 KHz. Usually, low-frequency RFID systems operate right around 125 KHz. The low-frequency band has a slower read speed than higher frequencies, but it has a greater ability to be transmitted or received in all directions.
low frequency rfid range

rfid lock system factory
samsung galaxy s10 plus wallet case with rfid protection
Mario Kart 8 Deluxe NFC Coins Card Set of 20 For switch. Opens in a new window or tab. .
uhf rfid is beeter than rfid only|high frequency rfid 12 inch