smart card baud rate This application note describes the fundamentals of the contact type smart cards, and how they are communi-cated using the PIC microcontroller. It also explains the T = 0 and T = 1 protocols, which are widely used in contact type smart card communications.
If this is the case, you may want to check the following: • Make sure the device has the latest software update. • Check the device’s NFC settings are enabled. • Make sure the device is not .
0 · Smartcard Library Overview
1 · Smart Card Operation Using Freescale
2 · Answer to reset
Photo by 12photostory on Unsplash. Step-1: Add NFC Permission to AndroidManifest.xml. To use NFC in your Android app, you need to add the NFC permission to your AndroidManifest.xml file. Open your .
The Smartcard default baudrate divider is 372, which produce 9600 bps when a clock signal of 3.57MHz is supplied to the card. Most Smartcards allow higher clock rates, so a simple 4MHz clock can be easily used. Using a 4MHz clock, the default baudrate comes out to be 10752 bps.
The standard defining the ATR in asynchronous transmission is ISO/IEC 7816-3. Subsets of the full ATR specification are used for some Smart Card applications, e.g. EMV. In asynchronous transmission, the ATR is transmitted by a card to a reader as characters, encoded as bits over the contact designated I/O (C7), with a nominal bit duration denoted Elementary Time Unit (ETU), equal during the whole ATR to 372 periods of the clock signal sup.The Smartcard default baudrate divider is 372, which produce 9600 bps when a clock signal of 3.57MHz is supplied to the card. Most Smartcards allow higher clock rates, so a simple 4MHz clock can be easily used. Using a 4MHz clock, the default baudrate comes out to be 10752 bps.
An Answer To Reset (ATR) is a message output by a contact Smart Card conforming to ISO/IEC 7816 standards, following electrical reset of the card's chip by a card reader. The ATR conveys information about the communication parameters proposed .ISO7816-3 describes smart card electric signals and transmission protocols, the detail can refer to the spec, below are some examples about for better understanding about the spec, 1, ATR and Baud Rate
This application note describes the fundamentals of the contact type smart cards, and how they are communi-cated using the PIC microcontroller. It also explains the T = 0 and T = 1 protocols, which are widely used in contact type smart card communications.TAi TBi TCi encodes the clock rate conversion integer (Fi), the value of the baud rate adjustment integer (Di), the maximum value of the frequency supported (f max), and extra guide time (N). Historical bytes The card and the reader have their own set of restrictions concerning baud rates; the card indicates its capabilities in the ATR, and the reader tries one of these in a process called PPS (protocol and parameter selection).Parameters such as protocol format, type of smart card, baud rate and other electrical parameters are read out of the smart card right after reset. This is known as the Answer to Reset or ATR.
The Baud rate generator in SERCOM module generates internal clocks for asynchronous and synchronous communication. The output frequency (f BAUD ) is determined by the Baud register (BAUD)
You don't need to change the clock rate that high (and it certainly wouldn't be supported by the card). You simply need to adjust Fi and Di, indeed. Here is an extract from the ISO7816-3 spec: To reach ~115200 bauds, typically, you'll choose Fi=512 (F=9) and Di=32 (D=5). Smart cards use the ISO7816-3 standard to communicate with the outside world. Smart cards need clocks which must be between 1MHz to 5MHz. This clock will be used to generate a baudrate with a fraction that is implemented in the card as default.The Smartcard default baudrate divider is 372, which produce 9600 bps when a clock signal of 3.57MHz is supplied to the card. Most Smartcards allow higher clock rates, so a simple 4MHz clock can be easily used. Using a 4MHz clock, the default baudrate comes out to be 10752 bps.
An Answer To Reset (ATR) is a message output by a contact Smart Card conforming to ISO/IEC 7816 standards, following electrical reset of the card's chip by a card reader. The ATR conveys information about the communication parameters proposed .
ISO7816-3 describes smart card electric signals and transmission protocols, the detail can refer to the spec, below are some examples about for better understanding about the spec, 1, ATR and Baud Rate This application note describes the fundamentals of the contact type smart cards, and how they are communi-cated using the PIC microcontroller. It also explains the T = 0 and T = 1 protocols, which are widely used in contact type smart card communications.TAi TBi TCi encodes the clock rate conversion integer (Fi), the value of the baud rate adjustment integer (Di), the maximum value of the frequency supported (f max), and extra guide time (N). Historical bytes The card and the reader have their own set of restrictions concerning baud rates; the card indicates its capabilities in the ATR, and the reader tries one of these in a process called PPS (protocol and parameter selection).
Parameters such as protocol format, type of smart card, baud rate and other electrical parameters are read out of the smart card right after reset. This is known as the Answer to Reset or ATR.The Baud rate generator in SERCOM module generates internal clocks for asynchronous and synchronous communication. The output frequency (f BAUD ) is determined by the Baud register (BAUD) You don't need to change the clock rate that high (and it certainly wouldn't be supported by the card). You simply need to adjust Fi and Di, indeed. Here is an extract from the ISO7816-3 spec: To reach ~115200 bauds, typically, you'll choose Fi=512 (F=9) and Di=32 (D=5).
dell external usb keyboard with smart card reader
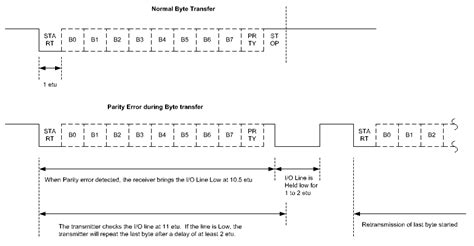
Smartcard Library Overview
S.A.S. WAKDEV CEO: Julien Veuillet Answering machine: +33.652283944 E .
smart card baud rate|Answer to reset