rfid card internal structure RFID tags are made of three different components: an RFID chip, which is an integrated circuit (IC), an antenna, and a substrate. A tag manufacturer typically does not make all three . The ACR1251U USB NFC Reader II offers advanced features such as firmware upgradeability, a SAM (Secure Access Module) slot, and support for NFC tags and devices. It is ideal for contactless applications with added security .
0 · what is rfid inlay
1 · technology behind rfid cards
2 · rfid card process
3 · rfid card function
4 · rfid card frequency
5 · rfid card anatomy
6 · microchip rfid card
7 · high frequency rfid card
A simple way to check if your credit card has RFID technology is to visually .
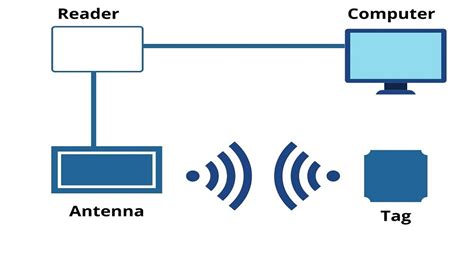
Inside An RFID Card. RFID cards communicate with card readers using electromagnetic frequencies. When a card is held within the electromagnetic field created by a card reader, the antenna draws power from the field and funnels it to the card’s Integrated Circuit (chip). This . The process involves the interaction between the card’s microchip and the reader’s antenna, facilitated by electromagnetic fields. Let’s delve into the details of how an RFID card .RFID tags are made of three different components: an RFID chip, which is an integrated circuit (IC), an antenna, and a substrate. A tag manufacturer typically does not make all three .Inside An RFID Card. RFID cards communicate with card readers using electromagnetic frequencies. When a card is held within the electromagnetic field created by a card reader, the antenna draws power from the field and funnels it to the card’s Integrated Circuit (chip). This powers on the card.
The process involves the interaction between the card’s microchip and the reader’s antenna, facilitated by electromagnetic fields. Let’s delve into the details of how an RFID card works: 1. The Reader and Antenna: The RFID reader consists of an antenna that generates an electromagnetic field.RFID tags are made of three different components: an RFID chip, which is an integrated circuit (IC), an antenna, and a substrate. A tag manufacturer typically does not make all three components in-house. The IC is typically designed and made by a semiconductor manufacturer, while an antenna is usually designed and made by a tag manufacturer.Although an RFID card may look ordinary, its internal structure contains many key technologies. The following are the main components of an RFID card: Chip: Chip is the core component of an RFID card, and its function is to store and process data information.RFID is a wireless communication technology that uses radio waves to achieve automatic identification and authentication. It is mainly achieved by adhering or embedding an RFID tag on the item, and the inside of the RFID tag is composed of an RFID microchip and antenna.
RFID tag explained: what’s inside an RFID label? The following three RFID components come together to form what we'd call an 'RFID inlay,' a super slim piece of technology that can be inserted into garments, stickers, or labels.RFID Block Schematic: A simplified block schematic of an RFID tag (also called transponder) is shown in the diagram below. Various components of the tag are as shown. Normally, the antenna is external to the tag chip, and large in size.These seven critical components play a major role in the functioning of any RFID system. Therefore, it only makes sense to diligently select these components with respect to target performance, accuracy, security, and end application.
By understanding these design principles, engineers and system integrators can create efficient, reliable, and secure RFID solutions tailored to specific application requirements.What's Inside an RFID Card? RFID cards are made up of three essential components: an antenna, a chip, and a substrate. The antenna is responsible for transmitting and receiving signals between the card and the reader. The chip stores the card's data and processes the signals received by the antenna, and the substrate is the material that holds .Inside An RFID Card. RFID cards communicate with card readers using electromagnetic frequencies. When a card is held within the electromagnetic field created by a card reader, the antenna draws power from the field and funnels it to the card’s Integrated Circuit (chip). This powers on the card.
The process involves the interaction between the card’s microchip and the reader’s antenna, facilitated by electromagnetic fields. Let’s delve into the details of how an RFID card works: 1. The Reader and Antenna: The RFID reader consists of an antenna that generates an electromagnetic field.RFID tags are made of three different components: an RFID chip, which is an integrated circuit (IC), an antenna, and a substrate. A tag manufacturer typically does not make all three components in-house. The IC is typically designed and made by a semiconductor manufacturer, while an antenna is usually designed and made by a tag manufacturer.Although an RFID card may look ordinary, its internal structure contains many key technologies. The following are the main components of an RFID card: Chip: Chip is the core component of an RFID card, and its function is to store and process data information.RFID is a wireless communication technology that uses radio waves to achieve automatic identification and authentication. It is mainly achieved by adhering or embedding an RFID tag on the item, and the inside of the RFID tag is composed of an RFID microchip and antenna.

what is rfid inlay
RFID tag explained: what’s inside an RFID label? The following three RFID components come together to form what we'd call an 'RFID inlay,' a super slim piece of technology that can be inserted into garments, stickers, or labels.RFID Block Schematic: A simplified block schematic of an RFID tag (also called transponder) is shown in the diagram below. Various components of the tag are as shown. Normally, the antenna is external to the tag chip, and large in size.These seven critical components play a major role in the functioning of any RFID system. Therefore, it only makes sense to diligently select these components with respect to target performance, accuracy, security, and end application. By understanding these design principles, engineers and system integrators can create efficient, reliable, and secure RFID solutions tailored to specific application requirements.

arduino code for rfid reader

technology behind rfid cards
I use a MIFARE Classic NFC access card. Is there any way to clone my card on .
rfid card internal structure|technology behind rfid cards