rfid reader memory The TID or Tag Identifier is 20 bytes or 160 bits. These means there are 1,460,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 different possible tag IDs (1.46 * 1048). More than there are atoms in the human body! Not quite the number of atoms in the universe. Every RFID tag has a . See more Digital Business Cards. Learn More. . Apple & Google Wallet. Learn More. .
0 · what is rfid memory
1 · rfid tag storage requirements
2 · rfid tag reader breakout
3 · rfid tag reader basics
4 · rfid tag memory
5 · rfid tag data storage
6 · rfid gen2 memory bank
7 · how to read rfid tags
Contactless payment is powered by RFID (Radio-frequency identification) technology and near-field communication (NFC). When you hold your card close—usually a few inches or so—to a card reader, its antenna .
The TID or Tag Identifier is 20 bytes or 160 bits. These means there are 1,460,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 different possible tag IDs (1.46 * 1048). More than there are atoms in the human body! Not quite the number of atoms in the universe. Every RFID tag has a . See moreWhile TIDs are good for absolute identification the Gen2 RFID standard was really created to replace the barcode in many retail . See more
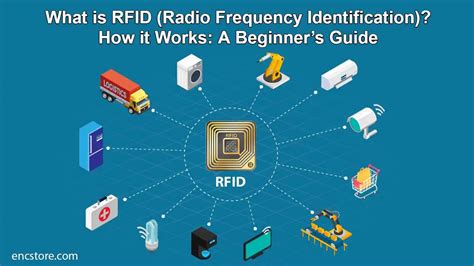
There are additional writable memory locations called the Access password and Kill password. The Access password can be used to prevent . See moreThe size of User Memory can vary from 0 bytes to 64 bytes. The cheaper the tag the fewer bytes of user memory it will likely have. What do you do with 64 bytes? To continue with the gallon-of-milk analogy, user memory was originally intended to record things like . See more Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a wireless technology that employs a set of RFID tags, an RFID reader, and a software system to wireless identify RFID-tagged items .Gen2 UHF RFID Memory Standard. The v2.0.1 standard written by EPCglobal covers all RFID requirements for Gen2 RFID tags. Generally speaking, the memory of a tag is split into three: the TID, EPC, and User Memory. Tag Identifier Memory. The TID .
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a wireless technology that employs a set of RFID tags, an RFID reader, and a software system to wireless identify RFID-tagged items and individuals without a clear line of sight. Depending upon the RFID system being used, the read range could be up to 100m.EPC Gen2 Reader Commands and Q Parameter. Understand memory layout for Gen2 UHF (RAIN) RFID tags including the memory banks for EPC, User Memory, Access and TID along with key commands for security.By considering factors such as EPC memory size, user memory size, memory retention, write cycles, and memory access control, you can choose an RFID label that meets your requirements for product tracking, inventory management, and supply chain operations.
In this article, we will cover everything you need to know about programming or encoding RFID tags including which RFID tag memory bank to use, which type of code to use - hex vs. ASCII, and how to determine how many characters you can encode.Tags have a small amount of memory that stores a unique tag identifier (TID), which is not editable. The little bit of data left on tags can be read-only or writeable, depending on how the tag was designed. You've no doubt seen RFID being used in everyday life - . Memory: The memory component in an RFID reader is used to store data temporarily or permanently. It can be used to store configuration settings, captured data, or any other relevant information required by the reader.An RFID card reader is a device that can read information stored on an RFID tag or card. It mainly consists of antennas, radio frequency modules, control units, and interface circuits.
At the most basic level, a finished RFID reader will include a processor, memory, power supply, antenna connectors, and a durable case built around an RFID reader module. Out of the box, a finished RFID reader is ready for deployment and, when paired with an RFID antenna, is capable of reading RFID tags. Reader modules are components of custom . An ultrahigh-frequency Gen 2 RFID tag carries business data in two memory banks: the EPC memory bank (also called the UII memory bank) and the user memory bank. (Two other memory banks hold control information and are not discussed here.) Most tags have at least 96 bits of EPC memory, many have 128 bits and a few have as much as 496 bits.
Gen2 UHF RFID Memory Standard. The v2.0.1 standard written by EPCglobal covers all RFID requirements for Gen2 RFID tags. Generally speaking, the memory of a tag is split into three: the TID, EPC, and User Memory. Tag Identifier Memory. The TID . Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a wireless technology that employs a set of RFID tags, an RFID reader, and a software system to wireless identify RFID-tagged items and individuals without a clear line of sight. Depending upon the RFID system being used, the read range could be up to 100m.EPC Gen2 Reader Commands and Q Parameter. Understand memory layout for Gen2 UHF (RAIN) RFID tags including the memory banks for EPC, User Memory, Access and TID along with key commands for security.By considering factors such as EPC memory size, user memory size, memory retention, write cycles, and memory access control, you can choose an RFID label that meets your requirements for product tracking, inventory management, and supply chain operations.
In this article, we will cover everything you need to know about programming or encoding RFID tags including which RFID tag memory bank to use, which type of code to use - hex vs. ASCII, and how to determine how many characters you can encode.Tags have a small amount of memory that stores a unique tag identifier (TID), which is not editable. The little bit of data left on tags can be read-only or writeable, depending on how the tag was designed. You've no doubt seen RFID being used in everyday life - . Memory: The memory component in an RFID reader is used to store data temporarily or permanently. It can be used to store configuration settings, captured data, or any other relevant information required by the reader.
omni rfid tags
An RFID card reader is a device that can read information stored on an RFID tag or card. It mainly consists of antennas, radio frequency modules, control units, and interface circuits.
what is rfid memory
At the most basic level, a finished RFID reader will include a processor, memory, power supply, antenna connectors, and a durable case built around an RFID reader module. Out of the box, a finished RFID reader is ready for deployment and, when paired with an RFID antenna, is capable of reading RFID tags. Reader modules are components of custom .
rfid card case wallet
rfid tag storage requirements
Go to the App Store. Search for “ NFC Tools.”. Once you’ve found the app, .
rfid reader memory|rfid tag storage requirements