low gain rfid read distance Antenna gain of 8 dBi or higher, is considered high gain; gain of 7 dBi or lower, is considered low gain. Linearly polarized antennas have a longer read range than circularly polarized antennas. Circularly polarized antennas are flexible in that they can read tags . Smartrac DF is equipped with the EM4423 chip that combines two functionalities on one single die: the EPC technology used for long-range application purposes, and the NFC technology used to exchange data in close .
0 · rfid tag reading distance
1 · rfid reading range
2 · rfid reading distance
3 · rfid chip reading distance
4 · how to improve rfid reading range
5 · how far rfid can be read
6 · how far can rfid be
7 · does rfid affect read range
Nathan King. 22. One of the legends of Auburn's basketball program will no longer be courtside in Neville Arena. Sonny Smith, who coached Auburn to five NCAA Tournaments .
Antenna gain of 8 dBi or higher, is considered high gain; gain of 7 dBi or lower, is considered low gain. Linearly polarized antennas have a longer read range than circularly polarized antennas. Circularly polarized antennas are flexible in that they can read tags . The read range of RFID tags refers to the maximum distance at which the .
Antenna gain of 8 dBi or higher, is considered high gain; gain of 7 dBi or lower, is considered low gain. Linearly polarized antennas have a longer read range than circularly polarized antennas. Circularly polarized antennas are flexible in that they can read tags oriented horizontally or vertically or even in between. The read range of RFID tags refers to the maximum distance at which the readers can successfully capture the data from the tags. Understanding the read range is crucial for implementing RFID systems effectively and optimizing their performance.Low frequency (LF) RFID chip. Operates between 30 and 300 kHz, the reading distance is shorter than high frequency (HF) and ultra high frequency (UHF), usually less than 10 cm. It is suitable for applications that need close distance and low interference. Here are some things I've considered: Ditch the embedded antenna on the cheap RFID reader and construct my own, larger antenna. I'd need to see if the onboard MFRC522 is up to the task of providing additional power. Look for a .
If you need less read range, use lower gain antennas. If you need to read tags up close, use very low gain proximity antennas. The details: Simply put, a higher gain antenna increases the power received from the reader. If you want to make sure your antennas have a longer “reach,” then you need high gain antennas (e.g. 9 dBi, or higher . The higher the antenna gain, the higher the read range. If you need to read RFID tags using a short read range, you should use low antenna gain. Why Antenna Gain is Crucial. This parameter is crucial since it gives you the power to regulate the read range.basic questions is how far away the reader can read data from these tags. This article provides a brief tutorial on the fac-tors affecting read range and a real-time,real-life de-sign example. The tutorial and design example are based on passive, 125-kHz to 13.56-MHz, induc-tively coupled RFID systems.The article focuses pri-
RFID is wireless technology that uses Radio Frequency (RF) electromagnetic energy to carry information between an RFID tag and an RFID reader. Some RFID systems will only work over a few inches (or centimetres) while others may work over 100 metres (300 feet) or more. Depending on the application and gate lay-out, you should determine what you need. For example, a high gain antenna is used when a long and directional detection area is required. A low gain antenna will generate an omnidirectional and short-range detection area.Many factors will affect the reading distance of RFID chips, including the following points: Frequency: RFID systems use different radio frequency frequencies such as low frequency (LF), high frequency (HF), ultra high frequency (UHF) and microwave frequency (MW). Antenna gain of 8 dBi or higher, is considered high gain; gain of 7 dBi or lower, is considered low gain. Linearly polarized antennas have a longer read range than circularly polarized antennas. Circularly polarized antennas are flexible in that they can read tags oriented horizontally or vertically or even in between.
The read range of RFID tags refers to the maximum distance at which the readers can successfully capture the data from the tags. Understanding the read range is crucial for implementing RFID systems effectively and optimizing their performance.Low frequency (LF) RFID chip. Operates between 30 and 300 kHz, the reading distance is shorter than high frequency (HF) and ultra high frequency (UHF), usually less than 10 cm. It is suitable for applications that need close distance and low interference.
Here are some things I've considered: Ditch the embedded antenna on the cheap RFID reader and construct my own, larger antenna. I'd need to see if the onboard MFRC522 is up to the task of providing additional power. Look for a .If you need less read range, use lower gain antennas. If you need to read tags up close, use very low gain proximity antennas. The details: Simply put, a higher gain antenna increases the power received from the reader. If you want to make sure your antennas have a longer “reach,” then you need high gain antennas (e.g. 9 dBi, or higher . The higher the antenna gain, the higher the read range. If you need to read RFID tags using a short read range, you should use low antenna gain. Why Antenna Gain is Crucial. This parameter is crucial since it gives you the power to regulate the read range.basic questions is how far away the reader can read data from these tags. This article provides a brief tutorial on the fac-tors affecting read range and a real-time,real-life de-sign example. The tutorial and design example are based on passive, 125-kHz to 13.56-MHz, induc-tively coupled RFID systems.The article focuses pri-
RFID is wireless technology that uses Radio Frequency (RF) electromagnetic energy to carry information between an RFID tag and an RFID reader. Some RFID systems will only work over a few inches (or centimetres) while others may work over 100 metres (300 feet) or more. Depending on the application and gate lay-out, you should determine what you need. For example, a high gain antenna is used when a long and directional detection area is required. A low gain antenna will generate an omnidirectional and short-range detection area.
smart ration card punjab list
rfid tag reading distance
smart sim card loader
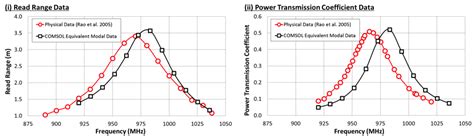
rfid reading range
ARBY's Grand Opening at Town Center Dr. Covington GA in Febuary. Arby's Store #9054 Grand Opening Live Radio Remote with THE KING Saturday, February 24th, 2024, Covington, GA - AES LLC / L.A. Media in collaboration .
low gain rfid read distance|how to improve rfid reading range