writable rfid chips user memory In the world of RFID technology, memory plays a crucial role in the functionality and versatility of tags. One type of user memory, re-writable RFID tags, offers the unique ability to update data multiple times, making them an ideal solution for applications requiring dynamic . FIDOを発見する . TapID(tm) Mobile Account FIDO U2F NFC Security Card; TapID(tm) .
0 · uhf rfid memory types
1 · uhf rfid memory bank
2 · rfid tags memory
3 · ics rfid tags memory
4 · ics rfid tags
See the latest NFL Standings by Division, Conference and League. Find current or past season NFL standings by team.Find out which teams are winning the 2024 playoff race. Check out the NFL Playoff Picture for .
Gen 2 UHF RFID tags are comprised of an antenna and a chip (more accurately called an integrated circuit, or IC). In this article, we will walk through the 4 memory banks on . In the world of RFID technology, memory plays a crucial role in the functionality and versatility of tags. One type of user memory, re-writable RFID tags, offers the unique ability to update data multiple times, making them an ideal solution for applications requiring dynamic .
Gen 2 UHF RFID tags are comprised of an antenna and a chip (more accurately called an integrated circuit, or IC). In this article, we will walk through the 4 memory banks on the IC inside of a UHF RFID tag and when to use each. In the world of RFID technology, memory plays a crucial role in the functionality and versatility of tags. One type of user memory, re-writable RFID tags, offers the unique ability to update data multiple times, making them an ideal solution for .When it comes to user memory, there is no standard on the number of memory bits that can be written to each Tag. One of the most popular chips with good user memory is the Monza 4QT, with 512 bits. However, there are some RFID Tags with much larger user memory, up to .
What is User Memory? It is considered as a second writable memory bank in UHF RFID tags. The typical length of user memory is 512 bits; however, some of them may reach up to 4k, and 8kB depending upon the usage. The user memory becomes only useful when the user needs memory more than EPC memory. There are only two writable memory banks on a Gen2 UHF RFID tag – the EPC memory and the user memory. Because the EPC memory bank is the main writable memory on an RFID tag, by default, the RFID reader will read the EPC memory.Understand memory layout for Gen2 UHF (RAIN) RFID tags including the memory banks for EPC, User Memory, Access and TID along with key commands for security.When it comes to user memory, there is no standard in how many bits of memory are writable on each tag. Typically, the extended memory is no more than 512 bits, but there are some high memory tags with up to 4K or 8K bytes of memory. This is .
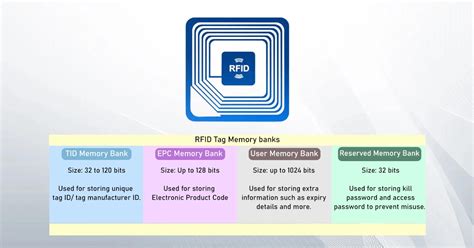
UHF Gen 2 RFID tags have four memory banks: EPC TID User Reserved The chipset, or integrated circuit (IC), houses these four memory banks and is where all the data is stored. Some chipsets have different bit allocations between the four banks to allow for more user memory or a longer EPC number. UHF RFID tags are characterized by various types of memory that are used for different purposes and functionalities. Each UHF Gen2 tag is equipped with an antenna and an IC (Integrated Circuit) containing four types of memory: Reserved memory. EPC memory. TID memory. User memory.
UHF Gen 2 RFID tags have four memory banks: 1. EPC. 2. TID. 3. USER. 4. Reserved. EPC Memory: The memory bank stores an EPC code or an electronic product code. It’s a minimum of 96 bits of writable memory. If most applications require only 96 bits of memory, EPC memory is typically used. Gen 2 UHF RFID tags are comprised of an antenna and a chip (more accurately called an integrated circuit, or IC). In this article, we will walk through the 4 memory banks on the IC inside of a UHF RFID tag and when to use each. In the world of RFID technology, memory plays a crucial role in the functionality and versatility of tags. One type of user memory, re-writable RFID tags, offers the unique ability to update data multiple times, making them an ideal solution for .
When it comes to user memory, there is no standard on the number of memory bits that can be written to each Tag. One of the most popular chips with good user memory is the Monza 4QT, with 512 bits. However, there are some RFID Tags with much larger user memory, up to .What is User Memory? It is considered as a second writable memory bank in UHF RFID tags. The typical length of user memory is 512 bits; however, some of them may reach up to 4k, and 8kB depending upon the usage. The user memory becomes only useful when the user needs memory more than EPC memory.
There are only two writable memory banks on a Gen2 UHF RFID tag – the EPC memory and the user memory. Because the EPC memory bank is the main writable memory on an RFID tag, by default, the RFID reader will read the EPC memory.Understand memory layout for Gen2 UHF (RAIN) RFID tags including the memory banks for EPC, User Memory, Access and TID along with key commands for security.When it comes to user memory, there is no standard in how many bits of memory are writable on each tag. Typically, the extended memory is no more than 512 bits, but there are some high memory tags with up to 4K or 8K bytes of memory. This is .
uhf rfid memory types
UHF Gen 2 RFID tags have four memory banks: EPC TID User Reserved The chipset, or integrated circuit (IC), houses these four memory banks and is where all the data is stored. Some chipsets have different bit allocations between the four banks to allow for more user memory or a longer EPC number. UHF RFID tags are characterized by various types of memory that are used for different purposes and functionalities. Each UHF Gen2 tag is equipped with an antenna and an IC (Integrated Circuit) containing four types of memory: Reserved memory. EPC memory. TID memory. User memory.
scan smart card
uhf rfid memory bank
rfid tags memory
Nfc-frog supports multiple modes for reading card data. See more
writable rfid chips user memory|ics rfid tags memory