chip rfid 2018 Microchip implants are going from tech-geek novelty to genuine health tool—and you might be running out of good reasons to say no. By Haley Weiss. Professor Kevin Warwick holds up an . Your business moves fast, but your custom business card and online experience keep all your customers, connections and partners up to date. You can update your site . See more
0 · where are rfid chips used
1 · types of rfid chips
2 · rfid chips in humans
3 · rfid chips for sale
4 · rfid chip pros and cons
5 · rfid chip meaning
6 · rfid chip manufacturing
7 · pros and cons of rfid
Visit ESPN for the complete 2024 NFL season Playoff standings. Includes winning percentage, home and away record, and current streak.
Microchip implants are going from tech-geek novelty to genuine health tool—and you might be running out of good reasons to say no. By Haley Weiss. Professor Kevin Warwick holds up an .June 7, 2018. Biohacking is the new frontier. In just a few years, millions of people will have implanted RFID chips under the skin between their thumb and index finger. Already, .
Microchip implants are going from tech-geek novelty to genuine health tool—and you might be running out of good reasons to say no. By Haley Weiss. Professor Kevin Warwick holds up an RFID .June 7, 2018. Biohacking is the new frontier. In just a few years, millions of people will have implanted RFID chips under the skin between their thumb and index finger. Already, thousands of.opment for networked RFID, low-cost, mass-manufacturing techniques for transponder hardware and energy efficient chip design. An estimated 16 billion passive RFID tags (LF, HF, and UHF) have been sold in 2018 to a wide range of industries and businesses including consumer goods tracking, apparel tag- The team worked each chip into an RFID tag with a standard radio-frequency antenna. In a key step, the researchers built a simple circuit around the memory chip, enabling the chip to switch to a local energy-assisted mode only when it senses a certain stimuli.
A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being. The purpose of this paper is to explore the benefits and barriers of implementing radio-frequency identification (RFID) technology in the healthcare sector and to provide recommendations to overcome potential barriers.Study 15-01-2018. This paper explains the technology of RFID chip implants; explores current applications, and considers legal, ethical, health, and security issues relating to their potential use in the workplace.
RFID chips (wearable or implanted) would work best at electro-chemical biosensing of bodily functions like monitoring glucose or cholesterol levels as well as body temperature or heart function (care context) (Masters & Michael, 2007; Xiang et al., 2022, p. 7).Through a literature review, this paper attempts to explore the challenges of RFID adoption in healthcare, with a focus on patient safety. Our main findings suggest that high costs of adoption, concerns related to security and privacy, and human safety risks are .This paper presents the current state of the RFID chip set market and argues that these offerings fall short of what is required from a genuine RFID solution-on-chip (SoC). Alternatives, including a genuine RFID SoC and dedicated RFID ASIC implementing anticollision algorithms are proposed. Microchip implants are going from tech-geek novelty to genuine health tool—and you might be running out of good reasons to say no. By Haley Weiss. Professor Kevin Warwick holds up an RFID .
June 7, 2018. Biohacking is the new frontier. In just a few years, millions of people will have implanted RFID chips under the skin between their thumb and index finger. Already, thousands of.opment for networked RFID, low-cost, mass-manufacturing techniques for transponder hardware and energy efficient chip design. An estimated 16 billion passive RFID tags (LF, HF, and UHF) have been sold in 2018 to a wide range of industries and businesses including consumer goods tracking, apparel tag-
The team worked each chip into an RFID tag with a standard radio-frequency antenna. In a key step, the researchers built a simple circuit around the memory chip, enabling the chip to switch to a local energy-assisted mode only when it senses a certain stimuli.A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being. The purpose of this paper is to explore the benefits and barriers of implementing radio-frequency identification (RFID) technology in the healthcare sector and to provide recommendations to overcome potential barriers.Study 15-01-2018. This paper explains the technology of RFID chip implants; explores current applications, and considers legal, ethical, health, and security issues relating to their potential use in the workplace.
RFID chips (wearable or implanted) would work best at electro-chemical biosensing of bodily functions like monitoring glucose or cholesterol levels as well as body temperature or heart function (care context) (Masters & Michael, 2007; Xiang et al., 2022, p. 7).Through a literature review, this paper attempts to explore the challenges of RFID adoption in healthcare, with a focus on patient safety. Our main findings suggest that high costs of adoption, concerns related to security and privacy, and human safety risks are .
nadra smart card fee and time
where are rfid chips used
nationwide smart card balance
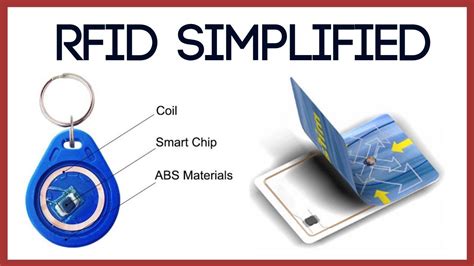
types of rfid chips
Be inspired with our fully customizable design templates. MOO US. MOO. .
chip rfid 2018|rfid chips in humans