low frequency lf passive rfid tags The LF tags are passive tags (no battery and transmitter on the tag) and have a short read range of a few inches. They have the lowest data transfer rate among all the RFID frequencies and usually store a small amount of data.
For NFC payments to work, someone has to hold their mobile device or tap-to-pay card close to an NFC-enabled reader. The reader then uses NFC technology to search for and identify that payment device. Once it finds .
0 · rfid frequency chart
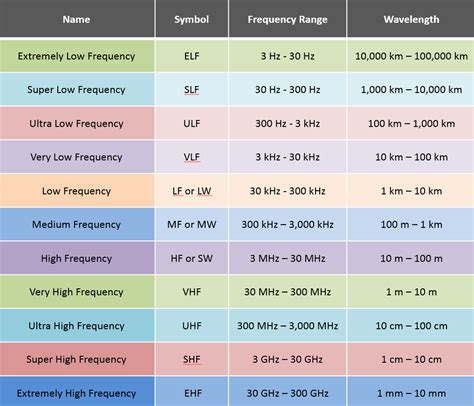
1 · rf frequency range chart
2 · low frequency rfid range
3 · disposable high frequency rfid tags
4 · difference between rfid labels
5 · 13 56 mhz rfid tag
6 · 125khz rfid tags
7 · 125khz rfid tag sticker
To create an automation: [9] Open the Shortcuts app. Tap the Automations tab at the bottom of the screen. Tap Create Personal Automation. Scroll down and tap NFC. Select Scan next to NFC Tag and hold your phone .
RFID, Inc.'s 125 KHz LF passive RFID Tags offerings run the gamut from rough tough .Passive RFID tags operate within specific frequency ranges, which affect their performance and applications. The main frequency ranges include: Low Frequency (LF): Operating between 30 kHz and 300 kHz, with most LF tags functioning at 125 kHz or 134 kHz. These tags have a short read range, typically only a few inches, making them suitable for .RFID, Inc.'s 125 KHz LF passive RFID Tags offerings run the gamut from rough tough hardened industrial, high temp, metal mount, in metal mount, to simple labels and stickers. Low-frequency (LF) RFID tags: 30 KHz to 300 KHz. LF RFID tags have slower read rates and shorter read ranges than UHF or HF, but they’re less susceptible to interference by liquids and metals because they have a longer wavelength.
Low Frequency RFID & High Frequency RFID have 8 key differences that set them apart - the actual frequency range , data rates, write capabilities, environmental concerns, read range, tag formats, RFID applications, RFID hardware.The LF tags are passive tags (no battery and transmitter on the tag) and have a short read range of a few inches. They have the lowest data transfer rate among all the RFID frequencies and usually store a small amount of data.
Passive RFID tags have low manufacturing costs because they do not require built-in batteries, which simplifies the production process. This design not only reduces production costs, but also makes the tags more economical when applied on a large scale.This passive low frequency RFID tag is ideal for laundry applications, supply chain management, inventory control, asset tracking, and process control. Low Frequency: Low Frequency (LF) RFID is emitted in the 30 - 300 kHz range, but most LF tags primarily operate on the 125 kHz band (specific frequency band) or the 134 kHz band. 2.6 Compatibility. 2.7 Cost-effectiveness. 3 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Understanding RFID Tag Types. There are a variety of RFID tags on the market, and their frequency range generally distinguishes them. RFID tag types can be classified as low-frequency, high-frequency, and ultra-high-frequency.
Types of Passive RFID Tags. There are three primary frequency ranges used for passive RFID systems: Low Frequency (LF) 125 KHz to 136 KHz. Short Range Reading (contact – ~ 3”) Magnetic Coupling. Applications include Access Control, Key FOBs, Animal Tracking. High Frequency (HF) 13.56 MHz. Medium Range Reading (contact – ~ 10”) Magnetic Coupling.Passive RFID tags operate within specific frequency ranges, which affect their performance and applications. The main frequency ranges include: Low Frequency (LF): Operating between 30 kHz and 300 kHz, with most LF tags functioning at 125 kHz or 134 kHz. These tags have a short read range, typically only a few inches, making them suitable for .RFID, Inc.'s 125 KHz LF passive RFID Tags offerings run the gamut from rough tough hardened industrial, high temp, metal mount, in metal mount, to simple labels and stickers. Low-frequency (LF) RFID tags: 30 KHz to 300 KHz. LF RFID tags have slower read rates and shorter read ranges than UHF or HF, but they’re less susceptible to interference by liquids and metals because they have a longer wavelength.
Low Frequency RFID & High Frequency RFID have 8 key differences that set them apart - the actual frequency range , data rates, write capabilities, environmental concerns, read range, tag formats, RFID applications, RFID hardware.
rfid frequency chart
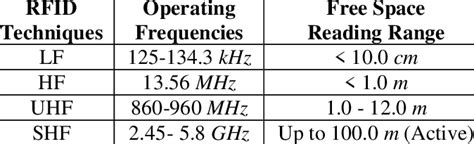
rf frequency range chart
The LF tags are passive tags (no battery and transmitter on the tag) and have a short read range of a few inches. They have the lowest data transfer rate among all the RFID frequencies and usually store a small amount of data.Passive RFID tags have low manufacturing costs because they do not require built-in batteries, which simplifies the production process. This design not only reduces production costs, but also makes the tags more economical when applied on a large scale.
This passive low frequency RFID tag is ideal for laundry applications, supply chain management, inventory control, asset tracking, and process control.
Low Frequency: Low Frequency (LF) RFID is emitted in the 30 - 300 kHz range, but most LF tags primarily operate on the 125 kHz band (specific frequency band) or the 134 kHz band. 2.6 Compatibility. 2.7 Cost-effectiveness. 3 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Understanding RFID Tag Types. There are a variety of RFID tags on the market, and their frequency range generally distinguishes them. RFID tag types can be classified as low-frequency, high-frequency, and ultra-high-frequency.
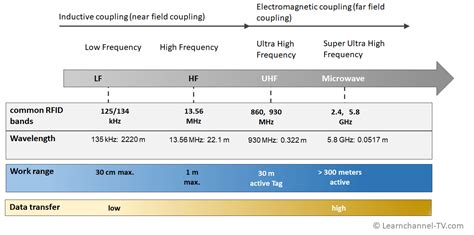
low frequency rfid range

how to apply rfid chip
Make NFC tags read-only. To prevent malicious users from overwriting an NFC tag's content, it is possible to make NFC tags permanently read-only. This operation is a one-way process and cannot be reversed. Once .
low frequency lf passive rfid tags|rf frequency range chart