how many gb does a rfid chip have Typically RFID chips are categorized according to their operating frequency range including ultra-high frequency (860MHz~960MHz), high frequency (13.56MHz), and low . If I understood correctly, your reader's current firmware is either TWN4_CK*.bix or TWN4_NK*.bix, where the K denotes a USB keyboard interface. Instead, you might want a .
0 · what is an rfid chip
1 · storage capacity of rfid tags
2 · storage capacity of rfid
3 · rfid memory capacity
4 · rfid frequency chart
5 · rfid chip specs
6 · how much rfid holds
7 · data storage rfid
What is NFC, and how does it work? NFC, which is short for near-field communication, is a technology that allows devices like phones and smartwatches to exchange small bits of data with other .
what is an rfid chip
Chip Size: The physical size of the RFID chip plays a role in determining the available memory capacity. Smaller chips might have limited memory capacity, while larger chips can accommodate more data storage.An RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) chip is a small device that uses radio waves to tra. Typically RFID chips are categorized according to their operating frequency range including ultra-high frequency (860MHz~960MHz), high frequency (13.56MHz), and low . Chip Size: The physical size of the RFID chip plays a role in determining the available memory capacity. Smaller chips might have limited memory capacity, while larger chips can accommodate more data storage.
Typically RFID chips are categorized according to their operating frequency range including ultra-high frequency (860MHz~960MHz), high frequency (13.56MHz), and low frequency (125 kHz). Now, let’s move further to understand more features of these RFID chips briefly: Ultrahigh Frequency RFID Chips (UHF RFID Chips) One of the simplest and most convenient methods to determine if a card is RFID or NFC enabled is by using a smartphone with NFC capabilities. With the widespread adoption of NFC technology in modern smartphones, this method allows you to quickly check if a card contains RFID or NFC technology. Specifications. There are multiple standard protocols controlled by ISO, IEC and EPCGlobal that have been established. A partial list is shown below. Check on line for current standards at each of these agencies. Some protocols are designated for specific use (animal tagging, or automotive industry for example).
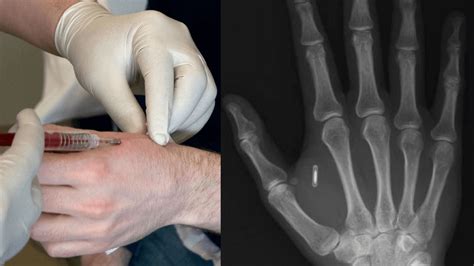
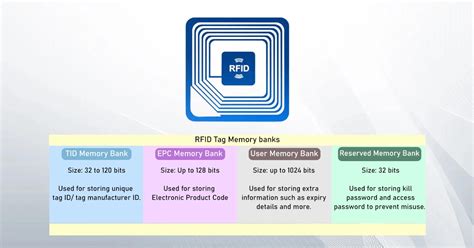
An RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) chip is a small device that uses radio waves to transmit data wirelessly. It consists of a microchip and an antenna, encapsulated in a tiny package. These chips are often embedded in various items, such as cards, tags, labels, or even implanted in living beings. RFID cards contain small computer chips that store up to 32 kilobytes of data. This space is enough to store a unique identification code for a specific individual. The data is encrypted, which prevents criminals from skimming it and using it for fraudulent activities. I understand that all RFID cards contain a UID in their memory from manufacture, normally in sector 0. But they also have additional sectors for data storage, my question is what is some example data that would be stored on these cards? In this article, we will cover everything you need to know about programming or encoding RFID tags including which RFID tag memory bank to use, which type of code to use - hex vs. ASCII, and how to determine how many characters you can encode.
RFID uses longer wavelengths on the slower end of the electromagnetic spectrum, which encompasses radio waves and microwaves. Within this range, RFID systems work within smaller subranges. For example, ultra-high frequency (UHF) wavelengths span 860-960 MHz, while Near Field Communication (NFC) uses high-frequency signals around 13 MHz. Active .Passive RFID tags typically store anywhere from 64 bits to 1 kilobyte of non-volatile memory. Originally, tags contained sufficient memory to store only a unique serial number or “license plate,” and perhaps some additional information. Chip Size: The physical size of the RFID chip plays a role in determining the available memory capacity. Smaller chips might have limited memory capacity, while larger chips can accommodate more data storage.
Typically RFID chips are categorized according to their operating frequency range including ultra-high frequency (860MHz~960MHz), high frequency (13.56MHz), and low frequency (125 kHz). Now, let’s move further to understand more features of these RFID chips briefly: Ultrahigh Frequency RFID Chips (UHF RFID Chips) One of the simplest and most convenient methods to determine if a card is RFID or NFC enabled is by using a smartphone with NFC capabilities. With the widespread adoption of NFC technology in modern smartphones, this method allows you to quickly check if a card contains RFID or NFC technology.
Specifications. There are multiple standard protocols controlled by ISO, IEC and EPCGlobal that have been established. A partial list is shown below. Check on line for current standards at each of these agencies. Some protocols are designated for specific use (animal tagging, or automotive industry for example).
An RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) chip is a small device that uses radio waves to transmit data wirelessly. It consists of a microchip and an antenna, encapsulated in a tiny package. These chips are often embedded in various items, such as cards, tags, labels, or even implanted in living beings.
RFID cards contain small computer chips that store up to 32 kilobytes of data. This space is enough to store a unique identification code for a specific individual. The data is encrypted, which prevents criminals from skimming it and using it for fraudulent activities.
I understand that all RFID cards contain a UID in their memory from manufacture, normally in sector 0. But they also have additional sectors for data storage, my question is what is some example data that would be stored on these cards? In this article, we will cover everything you need to know about programming or encoding RFID tags including which RFID tag memory bank to use, which type of code to use - hex vs. ASCII, and how to determine how many characters you can encode. RFID uses longer wavelengths on the slower end of the electromagnetic spectrum, which encompasses radio waves and microwaves. Within this range, RFID systems work within smaller subranges. For example, ultra-high frequency (UHF) wavelengths span 860-960 MHz, while Near Field Communication (NFC) uses high-frequency signals around 13 MHz. Active .
storage capacity of rfid tags

auburn football birmingham radio
To transfer your money faster than one to two business days, you have several .
how many gb does a rfid chip have|rfid memory capacity