smart card trusted roots For sign-in to work in a smart card-based domain, the smart card certificate . List via AuburnTigers.com of radio stations across the South that air Auburn football games.. Auburn Football Radio Affiliates {}Abbeville WESZ-FM 98.7 {}Greenville .
0 · view certs on smart card
1 · smart card trusted roots store
2 · smart card log on certificate
3 · smart card certificate authentication
4 · read certificate from smart card
5 · manage smart card certificates
6 · join domain with smart card
7 · import certificates from smart card
Near-field communication (NFC) is a short-range wireless connectivity .
You can enable a smart card logon process with Microsoft Windows 2000 and a non-Microsoft certification authority (CA) by following the guidelines in this . See more Discover the Group Policy, registry key, local security policy, and credential .
For sign-in to work in a smart card-based domain, the smart card certificate . Export or download the third-party root certificate. How to obtaining the party root certificate varies by vendor. The certificate must be in Base64 Encoded X.509 format. Add the third-party root CA to the trusted roots in an Active Directory Group Policy object. Discover the Group Policy, registry key, local security policy, and credential delegation policy settings that are available for configuring smart cards. For sign-in to work in a smart card-based domain, the smart card certificate must meet the following conditions: The KDC root certificate on the smart card must have an HTTP CRL distribution point listed in its certificate; The smart card sign-in certificate must have the HTTP CRL distribution point listed in its certificate
I used different little tools to see informations (ATR etc.) about my smartcard and they all worked out. I can see a lot of certificates there, but the one from my smartcard is missing in the store. The folder 'Smartcard trusted Roots' is empty.All certificates in the chain of trust Enhanced Key Usage field assert Smart Card Logon (OID 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.20.2.2) and Client Authentication (OID 1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.2). Best practice is for the root trust point certificate not to include an Enhanced Key Usage extension.When a user inserts a smart card, the Certificate Propagation service copies any root certificates on the card to the Smart Card Trusted Roots certificate stores on the local computer. This process establishes a trust relationship with the organization.
For non-domain-joined systems, the root CA of the KDC’s certificate is in the Third-Party Root CA or Smart Card Trusted Roots store. KDC’s certificate has the KDC EKU. KDC certificate’s DNSName field of the subjectAltName (SAN) extension matches the DNS name of . Unlike a password, a smart card can guarantee that authentication secrets are cryptographically strong and cannot be written down, lost, shared, “phished” or re-used in an insecure system. More generally, asymmetric cryptography can help eliminate the need for attack-able, locally stored authenticators and server-side password databases.When a smart card is inserted, the following steps are performed. Note. Unless otherwise mentioned, all operations are performed silently (CRYPT_SILENT is passed to CryptAcquireContext). The smart card resource manager database searches for the smart card's cryptographic service provider (CSP).Smart Card Trusted Roots (SmartCardRoot) — This container is used to store trusted smart card certificates. Other People (AddressBook) — This container maintains certificates that have been added to an Outlook contact.
Export or download the third-party root certificate. How to obtaining the party root certificate varies by vendor. The certificate must be in Base64 Encoded X.509 format. Add the third-party root CA to the trusted roots in an Active Directory Group Policy object. Discover the Group Policy, registry key, local security policy, and credential delegation policy settings that are available for configuring smart cards.
For sign-in to work in a smart card-based domain, the smart card certificate must meet the following conditions: The KDC root certificate on the smart card must have an HTTP CRL distribution point listed in its certificate; The smart card sign-in certificate must have the HTTP CRL distribution point listed in its certificate I used different little tools to see informations (ATR etc.) about my smartcard and they all worked out. I can see a lot of certificates there, but the one from my smartcard is missing in the store. The folder 'Smartcard trusted Roots' is empty.All certificates in the chain of trust Enhanced Key Usage field assert Smart Card Logon (OID 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.20.2.2) and Client Authentication (OID 1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.2). Best practice is for the root trust point certificate not to include an Enhanced Key Usage extension.When a user inserts a smart card, the Certificate Propagation service copies any root certificates on the card to the Smart Card Trusted Roots certificate stores on the local computer. This process establishes a trust relationship with the organization.
For non-domain-joined systems, the root CA of the KDC’s certificate is in the Third-Party Root CA or Smart Card Trusted Roots store. KDC’s certificate has the KDC EKU. KDC certificate’s DNSName field of the subjectAltName (SAN) extension matches the DNS name of . Unlike a password, a smart card can guarantee that authentication secrets are cryptographically strong and cannot be written down, lost, shared, “phished” or re-used in an insecure system. More generally, asymmetric cryptography can help eliminate the need for attack-able, locally stored authenticators and server-side password databases.When a smart card is inserted, the following steps are performed. Note. Unless otherwise mentioned, all operations are performed silently (CRYPT_SILENT is passed to CryptAcquireContext). The smart card resource manager database searches for the smart card's cryptographic service provider (CSP).
90 meter smart card manager firefox
view certs on smart card
90s smart card
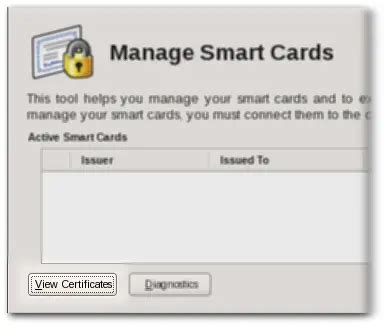
smart card trusted roots store
Listen online to Auburn Tigers Sports Network radio station for free – great choice for Auburn, United States. Listen live Auburn Tigers Sports Network radio with Onlineradiobox.com . cmon auburn we can win this game .
smart card trusted roots|manage smart card certificates