nfc frequency bands NFC communicating in one or both directions uses a frequency of 13.56 MHz in the globally available unlicensed radio frequency ISM band, compliant with the ISO/IEC 18000-3 air interface standard at data rates ranging from 106 to 848 kbit/s. See more Having the mux / relay between EMC filter and NFC IC bears the risk of EMC problems. The RFO outputs quite a fast rectangular signal. Thinking about Fourier, the .Posted on Nov 1, 2021 12:10 PM. On your iPhone, open the Shortcuts app. Tap on the Automation tab at the bottom of your screen. Tap on Create Personal Automation. Scroll down and select NFC. Tap on Scan. Put your iPhone near the NFC tag. Enter a name for your tag. .
0 · what is nfc chip
1 · what is nfc capability
2 · what frequency does nfc use
3 · what does nfc stand for
4 · nfc meaning in computer
5 · nfc how does it work
6 · nfc explanation
7 · nfc capabilities
The ACR122U NFC Reader is a PC-linked contactless smart card reader/writer developed based on 13.56 MHz Contactless (RFID) Technology. Compliant with the ISO/IEC18092 standard for Near Field Communication (NFC), it supports .
NFC communicating in one or both directions uses a frequency of 13.56 MHz in the globally available unlicensed radio frequency ISM band, compliant with the ISO/IEC 18000-3 air interface standard at data rates ranging from 106 to 848 kbit/s. See moreNear-field communication (NFC) is a set of communication protocols that enables communication between two electronic devices over a distance of 4 cm (1+1⁄2 in) or less. NFC offers a low-speed connection through . See moreAlthough the range of NFC is limited to a few centimeters, standard plain NFC is not protected against eavesdropping and can be vulnerable to data modifications. Applications may use higher-layer cryptographic protocols to establish a secure channel. See moreNFC allows one- and two-way communication between endpoints, suitable for many applications.NFC devices can act . See more
NFC standards cover communications protocols and data exchange formats and are based on existing radio-frequency identification (RFID) standards including ISO/IEC 14443 See more
NFC is rooted in radio-frequency identification technology (known as RFID) which allows compatible hardware to both supply power to and communicate with an otherwise . See moreNFC is a set of short-range wireless technologies, typically requiring a separation of 10 cm (3+7⁄8 in) or less. NFC operates at 13.56 See moreNFC standards cover communications protocols and data exchange formats, and are based on existing RFID standards including See more
NFC operates at a frequency of 13.56 MHz, a part of the high-frequency (HF) radio spectrum, and allows for both one-way and two-way communication between devices. However, its short .
NFC operates in a frequency range centered on 13.56 MHz and offers a data transmission rate of up to 424 kbit/s within a distance of approximately 10 centimeters.NFC communicating in one or both directions uses a frequency of 13.56 MHz in the globally available unlicensed radio frequency ISM band, compliant with the ISO/IEC 18000-3 air interface standard at data rates ranging from 106 to 848 kbit/s.NFC operates at a frequency of 13.56 MHz, a part of the high-frequency (HF) radio spectrum, and allows for both one-way and two-way communication between devices. However, its short range makes it ideal for secure, low-power exchanges. How NFC Works. NFC works by establishing a wireless link between two NFC-enabled devices.NFC operates in a frequency range centered on 13.56 MHz and offers a data transmission rate of up to 424 kbit/s within a distance of approximately 10 centimeters.
NFC operates within the globally available and unlicensed radio frequency ISM band of 13.56 MHz and can go up to a maximum data rate of 424Kb/s, whereas Bluetooth operates in the 2.4GHz.NFC operates in unlicensed ISM frequency band of about 13.56 MHz. It supports data rate of 106 Kbps , 212 kbps and 424 Kbps. NFC uses bandwidth of 14KHz to map data on the RF carrier.Near Field Communication (NFC) is a short-range wireless communication technology that has revolutionized how devices interact in various industries, from payments to data sharing. This NFC tutorial guide covers protocol stack, working principles, frame structure and different communication modes.Near-Field Communication, also known as NFC, is a type of RFID technology that operates on the 13.56 MHz frequency band. While the adaptation of NFC RFID can look very different from case to case, most NFC applications accomplish a similar goal .
NFC or Near Field Communications is a short-range wireless connectivity technology that allows two compatible devices to communicate without contact. This two-way wireless communication technology uses radio waves operating at a .
what is nfc chip
what is nfc capability


NFC frequency refers to the specific radio wave frequency at which NFC-enabled devices communicate. The 13.56 MHz frequency is globally accepted and standardized for NFC applications. This frequency band is a part of the high-frequency (HF) band of the radio spectrum and allows for a moderate data transfer rate and a small range of communication.
At its most basic level, near field communication is a standard for very short-range radio transmission. How short are we talking about? A pair of NFC transmitters can communicate at a maximum of just a few centimeters.
NFC communicating in one or both directions uses a frequency of 13.56 MHz in the globally available unlicensed radio frequency ISM band, compliant with the ISO/IEC 18000-3 air interface standard at data rates ranging from 106 to 848 kbit/s.
NFC operates at a frequency of 13.56 MHz, a part of the high-frequency (HF) radio spectrum, and allows for both one-way and two-way communication between devices. However, its short range makes it ideal for secure, low-power exchanges. How NFC Works. NFC works by establishing a wireless link between two NFC-enabled devices.
NFC operates in a frequency range centered on 13.56 MHz and offers a data transmission rate of up to 424 kbit/s within a distance of approximately 10 centimeters. NFC operates within the globally available and unlicensed radio frequency ISM band of 13.56 MHz and can go up to a maximum data rate of 424Kb/s, whereas Bluetooth operates in the 2.4GHz.NFC operates in unlicensed ISM frequency band of about 13.56 MHz. It supports data rate of 106 Kbps , 212 kbps and 424 Kbps. NFC uses bandwidth of 14KHz to map data on the RF carrier.Near Field Communication (NFC) is a short-range wireless communication technology that has revolutionized how devices interact in various industries, from payments to data sharing. This NFC tutorial guide covers protocol stack, working principles, frame structure and different communication modes.
Near-Field Communication, also known as NFC, is a type of RFID technology that operates on the 13.56 MHz frequency band. While the adaptation of NFC RFID can look very different from case to case, most NFC applications accomplish a similar goal . NFC or Near Field Communications is a short-range wireless connectivity technology that allows two compatible devices to communicate without contact. This two-way wireless communication technology uses radio waves operating at a .
NFC frequency refers to the specific radio wave frequency at which NFC-enabled devices communicate. The 13.56 MHz frequency is globally accepted and standardized for NFC applications. This frequency band is a part of the high-frequency (HF) band of the radio spectrum and allows for a moderate data transfer rate and a small range of communication.
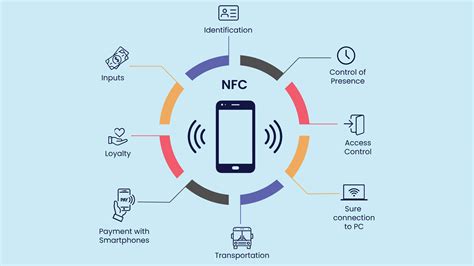
what frequency does nfc use
what does nfc stand for
The NFC API is an innovative tool that allows web applications to interact with NFC (Near Field Communication) devices. This technology opens up a world of .
nfc frequency bands|what frequency does nfc use