rfid lf hf uhf difference When choosing an RFID tag, one important but not-often-thought-of decision to make is the frequency of the tag, such as LF, HF or UHF. Which do you choose? low frequency (LF, 30 KHz to 300 kHz; typically LF systems work at 125 KHz) high frequency (HF, 3 to 30 MHz; typically HF systems work at 13.56 MHz) or; ultra high frequency (UHF, 300 MHZ to . $11.89
0 · uhf vs hf rfid
1 · rfid frequency
2 · rfid card vs uhf card
3 · low frequency rfid
4 · lf vs hf vs uhf
5 · lf vs hf frequency
6 · hf rf frequency
7 · difference between rfid and hf
For NFC payments to work, someone has to hold their mobile device or tap-to-pay card close to an NFC-enabled reader. The reader then uses NFC technology to search for and identify that payment device. Once it finds .
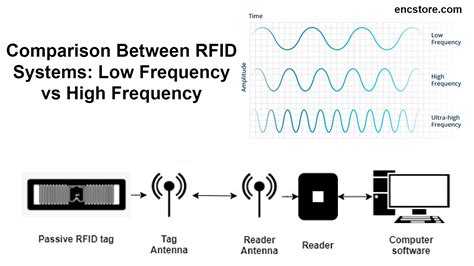
RFID operates across three primary frequency bands: Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra-High Frequency (UHF). In this guide, we’ll explore the characteristics of each band, their applications, and how to choose the one that best fits your needs.

When choosing an RFID tag, one important but not-often-thought-of decision to make is the frequency of the tag, such as LF, HF or UHF. Which do you choose? low frequency (LF, 30 KHz to 300 kHz; typically LF systems work at 125 KHz) high frequency (HF, 3 to 30 MHz; typically HF systems work at 13.56 MHz) or; ultra high frequency (UHF, 300 MHZ to .Ultra-high frequency tags have the highest data transmission rate against LF or HF. However, UHF is most susceptible to EMI and radio wave noise. Also, these tags are relatively easy to manufacture, and as such, they are cheaper than LF & HF tags.RFID systems throughout the world mainly operate in 3 different frequency bands: Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) bands. Radio waves behave differently at each of these frequencies and there are advantages and disadvantages associated with using each frequency band. Low Frequency (LF) RFID. What are RFID tags? Comparing ultra-high-frequency (UHF) vs. high-frequency (HF) vs. near field communication (NFC) vs. low-frequency (LF) RFID tag types. An explanation of the difference between active, passive and semi-passive RFID tags.
Reduce shrinkage and prevent inventory stock-outs. Secure access to specified areas or products. Improve overall business operations. Understanding the differences between HF and UHF RFID technology can change the way you do business and . Low Frequency RFID & High Frequency RFID have 8 key differences that set them apart - the actual frequency range , data rates, write capabilities, environmental concerns, read range, tag formats, RFID applications, RFID hardware.
Advantages: UHF frequencies have the longest transmission distance, usually between a few meters and more than ten meters, and have a high data transmission rate. This makes it ideal for applications such as supply chain management and vehicle tracking that . The three primary frequencies used with RFID devices include Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra High Frequency (UHF). But what’s the difference between these frequencies? Well, each of the three frequencies behaves differently when .
Choosing the right RFID tag may seem a simple task at first sight, but when it comes to maximizing the potential of its monitoring and identity systems, an element that often goes unnoticed is the frequency where these tags work.
RFID operates across three primary frequency bands: Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra-High Frequency (UHF). In this guide, we’ll explore the characteristics of each band, their applications, and how to choose the one that best fits your needs. When choosing an RFID tag, one important but not-often-thought-of decision to make is the frequency of the tag, such as LF, HF or UHF. Which do you choose? low frequency (LF, 30 KHz to 300 kHz; typically LF systems work at 125 KHz) high frequency (HF, 3 to 30 MHz; typically HF systems work at 13.56 MHz) or; ultra high frequency (UHF, 300 MHZ to .Ultra-high frequency tags have the highest data transmission rate against LF or HF. However, UHF is most susceptible to EMI and radio wave noise. Also, these tags are relatively easy to manufacture, and as such, they are cheaper than LF & HF tags.
RFID systems throughout the world mainly operate in 3 different frequency bands: Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) bands. Radio waves behave differently at each of these frequencies and there are advantages and disadvantages associated with using each frequency band. Low Frequency (LF) RFID. What are RFID tags? Comparing ultra-high-frequency (UHF) vs. high-frequency (HF) vs. near field communication (NFC) vs. low-frequency (LF) RFID tag types. An explanation of the difference between active, passive and semi-passive RFID tags.Reduce shrinkage and prevent inventory stock-outs. Secure access to specified areas or products. Improve overall business operations. Understanding the differences between HF and UHF RFID technology can change the way you do business and . Low Frequency RFID & High Frequency RFID have 8 key differences that set them apart - the actual frequency range , data rates, write capabilities, environmental concerns, read range, tag formats, RFID applications, RFID hardware.
Advantages: UHF frequencies have the longest transmission distance, usually between a few meters and more than ten meters, and have a high data transmission rate. This makes it ideal for applications such as supply chain management and vehicle tracking that . The three primary frequencies used with RFID devices include Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra High Frequency (UHF). But what’s the difference between these frequencies? Well, each of the three frequencies behaves differently when .

uhf vs hf rfid

homemade rfid protection
Head to Resident Services and interact with the Nook Stop terminal and select the Amiibo option. Tap your Amiibo or Amiibo Card on the NFC touchpoint (the joystick on the right joycon or the .
rfid lf hf uhf difference|uhf vs hf rfid