rfid tag low frequency If you are familiar with Passive UHF RFID tags, you are aware that these tags must be used with precautions around metal, liquids, and other difficult environmental factors. UHF RFID . See more •Carddass Baka Ichidai (archive) - Japanese site with images of all cards. See more
0 · rfid frequency chart
1 · rf frequency range chart
2 · low frequency rfid range
3 · disposable high frequency rfid tags
4 · difference between rfid labels
5 · 13 56 mhz rfid tag
6 · 125khz rfid tags
7 · 125khz rfid tag sticker
Near-Field Communication (NFC) is a radio-based contactless peer-to-peer communication protocol for exchange between devices at very close distances. Members Online • . We need a contactless ring that pairs or charges to a credit card so you can spend as you wish.
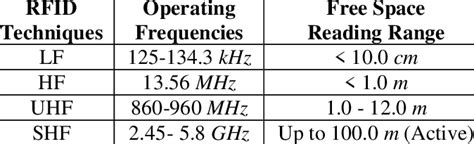
One of the most obvious differences between Low Frequency RFID and High Frequency RFID is the frequency range on which the tags and readers communicate. Low Frequency RFID typically operates between 125 kHz and 134 kHz, but the overall, larger range is between 30 kHz and 300 kHz. The actual . See moreData rates, also known as data-transfer rates, describe how fast the data from the tag can be transferred to the RFID reader. When comparing the data rates of Low Frequency RFID and . See more
Most High Frequency RFID tags, including NFC tags, have data that can be read and re-written hundreds of times, but the same cannot be . See moreBoth Low Frequency RFID and High Frequency RFID are short range RFID frequencies, and neither one can reliably read tags over 1 foot in read distance. In some RFID . See moreIf you are familiar with Passive UHF RFID tags, you are aware that these tags must be used with precautions around metal, liquids, and other difficult environmental factors. UHF RFID . See moreRFID tags are categorized according to the frequency at which they are designed to operate. Four primary frequency ranges are allocated by various government authorities for use by RFID .
One of the most obvious differences between Low Frequency RFID and High Frequency RFID is the frequency range on which the tags and readers communicate. Low Frequency RFID typically operates between 125 kHz and 134 kHz, but the overall, larger range is between 30 kHz and 300 kHz.RFID tags are categorized according to the frequency at which they are designed to operate. Four primary frequency ranges are allocated by various government authorities for use by RFID systems. • Low frequency (LF) • High frequency (HF) • Ultra high frequency (UHF) • Microwave frequency (microwave) Low-Frequency tags. Low Frequency (LF) tags generally operate at 125–134 kilohertz, meaning they usually have slower data transfer rates than their high-frequency or ultra-high frequency counterparts.
Low-frequency (LF) RFID tags: 30 KHz to 300 KHz. LF RFID tags have slower read rates and shorter read ranges than UHF or HF, but they’re less susceptible to interference by liquids and metals because they have a longer wavelength.Zheng. In the world of RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology, understanding the range of RFID tags is crucial for selecting the right system for your business needs. Whether you’re managing inventory, tracking assets, or controlling access, knowing how far an RFID tag can be read helps ensure you choose the most effective solution.Low Frequency (LF): 125 kHz – 134 kHz. Advantages: LF frequencies can penetrate water and metal, which makes them excellent in wet or metallic environments. For example, they are very reliable in animal tracking and certain factory automation applications. Low Frequency (LF) RFID. Characteristics: Frequency Range: 125 kHz or 134 kHz. Read Range: 10 cm to 1 meter (4 inches to 3 feet) Data Transfer Rate: Slow. Sensitivity to Interference: Less sensitive to interference from liquids and metals. Cost: Typically, higher than UHF systems. Applications:
High frequency, like low frequency, uses magnetic coupling to communicate between the tags and the RFID reader/antenna. HF waves can pass through most materials except for water and dense metals. Thin metals, like aluminum, can still be tagged with HF tags and function normally.Passive RFID tags operate within specific frequency ranges, which affect their performance and applications. The main frequency ranges include: Low Frequency (LF): Operating between 30 kHz and 300 kHz, with most LF tags functioning at 125 kHz or 134 kHz. These tags have a short read range, typically only a few inches, making them suitable for .
Low-frequency RFID operates at frequencies between 30 kHz and 300 kHz. This range allows shorter reading distances, typically up to 10 centimeters. LF RFID is commonly used for access control, animal tracking, and keyless entry systems. One of the most obvious differences between Low Frequency RFID and High Frequency RFID is the frequency range on which the tags and readers communicate. Low Frequency RFID typically operates between 125 kHz and 134 kHz, but the overall, larger range is between 30 kHz and 300 kHz.RFID tags are categorized according to the frequency at which they are designed to operate. Four primary frequency ranges are allocated by various government authorities for use by RFID systems. • Low frequency (LF) • High frequency (HF) • Ultra high frequency (UHF) • Microwave frequency (microwave) Low-Frequency tags. Low Frequency (LF) tags generally operate at 125–134 kilohertz, meaning they usually have slower data transfer rates than their high-frequency or ultra-high frequency counterparts.
Low-frequency (LF) RFID tags: 30 KHz to 300 KHz. LF RFID tags have slower read rates and shorter read ranges than UHF or HF, but they’re less susceptible to interference by liquids and metals because they have a longer wavelength.Zheng. In the world of RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology, understanding the range of RFID tags is crucial for selecting the right system for your business needs. Whether you’re managing inventory, tracking assets, or controlling access, knowing how far an RFID tag can be read helps ensure you choose the most effective solution.Low Frequency (LF): 125 kHz – 134 kHz. Advantages: LF frequencies can penetrate water and metal, which makes them excellent in wet or metallic environments. For example, they are very reliable in animal tracking and certain factory automation applications.
application of student smart card
Low Frequency (LF) RFID. Characteristics: Frequency Range: 125 kHz or 134 kHz. Read Range: 10 cm to 1 meter (4 inches to 3 feet) Data Transfer Rate: Slow. Sensitivity to Interference: Less sensitive to interference from liquids and metals. Cost: Typically, higher than UHF systems. Applications:
rfid frequency chart
High frequency, like low frequency, uses magnetic coupling to communicate between the tags and the RFID reader/antenna. HF waves can pass through most materials except for water and dense metals. Thin metals, like aluminum, can still be tagged with HF tags and function normally.
Passive RFID tags operate within specific frequency ranges, which affect their performance and applications. The main frequency ranges include: Low Frequency (LF): Operating between 30 kHz and 300 kHz, with most LF tags functioning at 125 kHz or 134 kHz. These tags have a short read range, typically only a few inches, making them suitable for .
apply for a smart card
rf frequency range chart
Click the app and simply hold your Leap Card to the back of your NFC-enabled Android smartphone to instantly check your balance, purchase or collect a pre-paid ticket, or .
rfid tag low frequency|low frequency rfid range