rfid card thickness The standard defines four card sizes: ID-1, ID-2, ID-3 and ID-000. All card sizes have a thickness of 760±80 μm, i.e. minimum 0.68 millimetres (0.027 in) and maximum 0.84 millimetres (0.033 in). The standard defines both metric and imperial measurements, noting that: Numeric values in the SI and/or . See more Find and press the “Connections” or “Network & Internet” option from the main Settings screen. F ind and pick the “NFC” option from here, or simply search for “tag” in your settings search bar if it is present. Simply flip .The PDM is essentially a locked down phone. All phones will generally create a response if it has an NFC reader. Even if it's not really reading any information. It just detects the signal. My guess is that you accidentally ran your pdm over something that was NFC capable. Reply.
0 · what does rfid card mean
1 · types of rfid cards
2 · technology behind rfid cards
3 · rfid card reading range
4 · rfid card reading distance
5 · rfid card anatomy
6 · how rfid card works
The NFC Working Group was closed after its charter expired (mainly due to lack of support by browser vendors) and is no longer maintaining the specification. Instead there is a NFC .
The standard defines four card sizes: ID-1, ID-2, ID-3 and ID-000. All card sizes have a thickness of 760±80 μm, i.e. minimum 0.68 millimetres (0.027 in) and maximum 0.84 millimetres (0.033 in). The standard defines both metric and imperial measurements, noting that: Numeric values in the SI and/or . See more

ISO/IEC 7810 Identification cards — Physical characteristics is an international standard that defines the physical characteristics for identification cards. See moreThe standard specifies requirements for such physical characteristics as:• Bending stiffness• Toxicity See more
• ISO/IEC 7811 defines traditional techniques for recording data on ID-1 identification cards, namely embossed characters and several different magnetic recording formats.• ISO/IEC 7816 defines ID-1 identification cards with an embedded chip ( See more
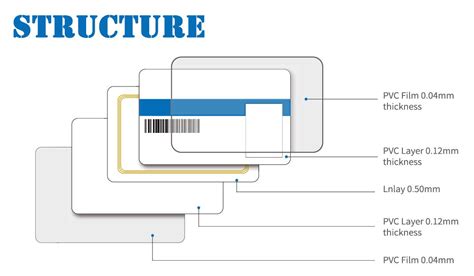
• ISO/IEC 7810:2019-12 See moreThe thickness of an RFID card varies from 0.5mm-1mm depending on the different production processes and customer needs. There are other dimensions available, which as known as customized dimensions. How RFID cards work .All card sizes have a thickness of 760 ± 80 μm, i.e. minimum 0.68 millimetres (0.027 in) and maximum 0.84 millimetres (0.033 in). The standard defines both metric and imperial measurements, noting that: [4]
The thickness of an RFID card varies from 0.5mm-1mm depending on the different production processes and customer needs. There are other dimensions available, which as known as customized dimensions. How RFID cards work depends on the interplay of three key components: the RFID card, the reader, and the backend data system. RFID card.The options specified defined RFID card Physical dimensions, that are various sizes of identification cards having a nominal thickness of 0.76 mm : ID-000 specifies a size of 25 mm * 15 mm, with the corner slightly (3mm) bevelled.Radio Frequency (RF) access credentials come in all shapes and sizes. From clamshell cards to key fobs and watches, these compact devices are loaded with data and offer access to an array of impressive applications.
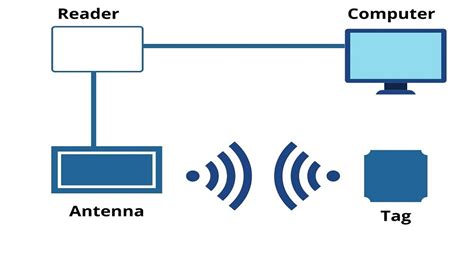
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) cards are used for tracking, identification, and access control. The cards integrate an RFID microchip that holds all the data needed for specific applications. An RFID card operates using a simple yet sophisticated technology that enables wireless communication with RFID readers. The process involves the interaction between the card’s microchip and the reader’s antenna, facilitated by electromagnetic fields.Learn the different components that go into an RFID Tag such as RFID chip, inlay, antenna and strap. Choosing the best RFID is important for any RFID project. RFID cards typically measure 85.60 by 53.98 millimeters (3 3⁄8″ × 2 1⁄8″) with rounded corners. RFID cards come in a range of thicknesses, typically from 0.5mm to 1mm. These depends on the production process and the specific requirements of the customer.
It can adapt to pH values from 0 to 14 and can be used in chemical industry scenarios such as medical devices, automotive industry and electronic fields. Explore the pivotal role of RFID metal tags in overcoming challenges of metal surface identification and enhancing IoT applications.An RFID card has a thin form factor (81x54x1 mm), like a driving license or identification card, and can be kept in the user's wallet. However, an RFID tag is smaller and thicker (around 20x20x5 mm) but can be kept in the user's keyring.
what does rfid card mean
All card sizes have a thickness of 760 ± 80 μm, i.e. minimum 0.68 millimetres (0.027 in) and maximum 0.84 millimetres (0.033 in). The standard defines both metric and imperial measurements, noting that: [4]The thickness of an RFID card varies from 0.5mm-1mm depending on the different production processes and customer needs. There are other dimensions available, which as known as customized dimensions. How RFID cards work depends on the interplay of three key components: the RFID card, the reader, and the backend data system. RFID card.The options specified defined RFID card Physical dimensions, that are various sizes of identification cards having a nominal thickness of 0.76 mm : ID-000 specifies a size of 25 mm * 15 mm, with the corner slightly (3mm) bevelled.Radio Frequency (RF) access credentials come in all shapes and sizes. From clamshell cards to key fobs and watches, these compact devices are loaded with data and offer access to an array of impressive applications.
rfid based attendance system using arduino uno
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) cards are used for tracking, identification, and access control. The cards integrate an RFID microchip that holds all the data needed for specific applications. An RFID card operates using a simple yet sophisticated technology that enables wireless communication with RFID readers. The process involves the interaction between the card’s microchip and the reader’s antenna, facilitated by electromagnetic fields.
Learn the different components that go into an RFID Tag such as RFID chip, inlay, antenna and strap. Choosing the best RFID is important for any RFID project.
rfid based library management system mini project
types of rfid cards
RFID cards typically measure 85.60 by 53.98 millimeters (3 3⁄8″ × 2 1⁄8″) with rounded corners. RFID cards come in a range of thicknesses, typically from 0.5mm to 1mm. These depends on the production process and the specific requirements of the customer.It can adapt to pH values from 0 to 14 and can be used in chemical industry scenarios such as medical devices, automotive industry and electronic fields. Explore the pivotal role of RFID metal tags in overcoming challenges of metal surface identification and enhancing IoT applications.
technology behind rfid cards
Search History. Clear History. Products. Support
rfid card thickness|technology behind rfid cards