key derivation smart card weakness This is where Key Derivation Functions (KDFs) like PBKDF2 (Password-Based Key Derivation Function 2) come into play. In this post, we’ll explore the benefits of using KDFs, . The lower screen has an NFC reader, so just tap to the screen. (I have a 2DSXL as well and .
0 · key derivation
1 · Visa, MasterCard, and EMV
2 · Understanding the Benefits of Key Derivation Functions: A Deep
3 · Understanding the Benefits of Key Deriv
4 · Secured Authentication Using Anonymity and Password
5 · SCP03
6 · Modern Key Derivation Functions
7 · Key derivation functions (KDF): What ar
8 · Key derivation function
9 · Evaluation of Authentication and Key Agreement Approaches of
10 · Elliptic Curve Cryptography in Practice
11 · Cryptography on smart cards
12 · Cryptanalysis and Improvement of ECC Based Authentication
I wrote a small Java (1.7+) program to dump (and write to) MiFare Classic 1K .
The maximum length of a single derived key should be less than the blocksize of the PRF used in PBKDF2 (to reduce exposure of the master key if a derived key is found). For example, if you used MD5 (bs of 128 bit) to generate a 256 bit key, if that 256 bit key was found (brute force, . The exploitation of system weaknesses of smart cards can be subdivided into internal and external attacks. For internal attacks the chip surface is studied and hence this .
This is where Key Derivation Functions (KDFs) like PBKDF2 (Password-Based Key Derivation Function 2) come into play. In this post, we’ll explore the benefits of using KDFs, .In June 2017, The U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) issued a new revision of their digital authentication guidelines, NIST SP 800-63B-3, [7]: 5.1.1.2 stating that: .Modern Key Derivation Functions. PBKDF2 has a major weakness: it is not GPU-resistant and not ASIC-resistant, because it uses relatively small amount of RAM and can be efficiently . Smart card is also vulnerable to impersonation attack, stolen smart card attack, offline password guessing attack and server masquerading attack. Additionally, smart card has .
We explore the deployment of elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) in practice by investigating its usage in Bitcoin, SSH, TLS, and the Austrian citizen card. More than a decade . Most of the multi-factor authentication and key exchange protocols in the literature, whether smart card or RFID based, rely on ECC for their security. Hence, an additional layer .Building on the foundation of the Evolved Packet System-AKA (EPS-AKA) protocol from the 4G-LTE network, the 5G-AKA protocol inherits some weaknesses, rendering it susceptible to .
Book 2, Annex A1.3 describes how a smart-card, card-specific session key is derived from a card-issuer-supplied PIN-block-encryption key (ENC-MDK). The encryption key is derived using a .The maximum length of a single derived key should be less than the blocksize of the PRF used in PBKDF2 (to reduce exposure of the master key if a derived key is found). For example, if you used MD5 (bs of 128 bit) to generate a 256 bit key, if that 256 bit key was found (brute force, or other weakness), the entire 128 bit output of a PBKDF2 . They both allow authentication and key exchange, before continuing with symmetric cryptography to communicate. Smart card industry is a very slow-paced world when it comes to upgrade since deployed hardware can't be upgraded (usually). The exploitation of system weaknesses of smart cards can be subdivided into internal and external attacks. For internal attacks the chip surface is studied and hence this requires opening of the card. This type of attack requires physical equipment rather than cryptographic know-how.
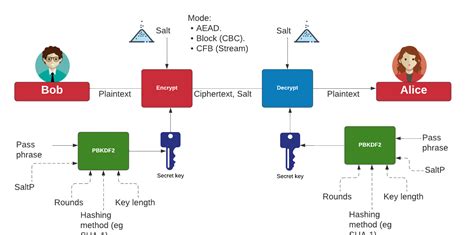
KDF's or Key Derivation Functions are functions or schemes to derive key or output keying material (OKM) from other secret information, the input keying material (IKM). That information may be another key or, for instance a password. This is where Key Derivation Functions (KDFs) like PBKDF2 (Password-Based Key Derivation Function 2) come into play. In this post, we’ll explore the benefits of using KDFs, particularly PBKDF2, for hashing values, highlighting how they enhance security in .
In June 2017, The U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) issued a new revision of their digital authentication guidelines, NIST SP 800-63B-3, [7]: 5.1.1.2 stating that: "Verifiers SHALL store memorized secrets [i.e. passwords] in .Modern Key Derivation Functions. PBKDF2 has a major weakness: it is not GPU-resistant and not ASIC-resistant, because it uses relatively small amount of RAM and can be efficiently implemented on GPU (graphics cards) or ASIC (specialized hardware). Smart card is also vulnerable to impersonation attack, stolen smart card attack, offline password guessing attack and server masquerading attack. Additionally, smart card has some limitation on deployment process because not all computer and devices could support the smart card reader. We explore the deployment of elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) in practice by investigating its usage in Bitcoin, SSH, TLS, and the Austrian citizen card. More than a decade after its first standardization, we find that this instantiation of .
Most of the multi-factor authentication and key exchange protocols in the literature, whether smart card or RFID based, rely on ECC for their security. Hence, an additional layer of defense should be added to them to guarantee increased security against MITM, database and clogging attacks.The maximum length of a single derived key should be less than the blocksize of the PRF used in PBKDF2 (to reduce exposure of the master key if a derived key is found). For example, if you used MD5 (bs of 128 bit) to generate a 256 bit key, if that 256 bit key was found (brute force, or other weakness), the entire 128 bit output of a PBKDF2 . They both allow authentication and key exchange, before continuing with symmetric cryptography to communicate. Smart card industry is a very slow-paced world when it comes to upgrade since deployed hardware can't be upgraded (usually).
read smart card reader
The exploitation of system weaknesses of smart cards can be subdivided into internal and external attacks. For internal attacks the chip surface is studied and hence this requires opening of the card. This type of attack requires physical equipment rather than cryptographic know-how.
key derivation
KDF's or Key Derivation Functions are functions or schemes to derive key or output keying material (OKM) from other secret information, the input keying material (IKM). That information may be another key or, for instance a password.
This is where Key Derivation Functions (KDFs) like PBKDF2 (Password-Based Key Derivation Function 2) come into play. In this post, we’ll explore the benefits of using KDFs, particularly PBKDF2, for hashing values, highlighting how they enhance security in .In June 2017, The U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) issued a new revision of their digital authentication guidelines, NIST SP 800-63B-3, [7]: 5.1.1.2 stating that: "Verifiers SHALL store memorized secrets [i.e. passwords] in .Modern Key Derivation Functions. PBKDF2 has a major weakness: it is not GPU-resistant and not ASIC-resistant, because it uses relatively small amount of RAM and can be efficiently implemented on GPU (graphics cards) or ASIC (specialized hardware).
prepaid smart simm card for philippines
Smart card is also vulnerable to impersonation attack, stolen smart card attack, offline password guessing attack and server masquerading attack. Additionally, smart card has some limitation on deployment process because not all computer and devices could support the smart card reader. We explore the deployment of elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) in practice by investigating its usage in Bitcoin, SSH, TLS, and the Austrian citizen card. More than a decade after its first standardization, we find that this instantiation of .
Visa, MasterCard, and EMV
If you encounter the “Couldn’t read NFC tag” error, it’s imperative to ensure that your device’s software is up to date, as software updates often include bug fixes, performance .
key derivation smart card weakness|Cryptanalysis and Improvement of ECC Based Authentication